Russia-Ukraine War
Iran’s Looming Missile Shipment to Russia: A Game-Changer in Ukraine’s War?

As Iran Prepares to Arm Russia with Ballistic Missiles, Could We Be Witnessing the Start of a New Escalation in Global Conflict?
Iran is reportedly gearing up to supply Russia with hundreds of ballistic missiles, marking a dramatic escalation in the already tense geopolitical landscape. According to European intelligence sources, this arms transfer involves the Fath-360 close-range ballistic missile system—an advanced weapon that could give Russian forces a new edge on the battlefield. And while Moscow’s military is no stranger to ballistic missiles, the infusion of Iranian technology might just be the spark that ignites a broader, more devastating phase of the war.
What’s more, this isn’t just a case of shipping weapons across borders. Reports suggest that Russian military personnel have been on the ground in Iran, training to operate these missile systems—a clear signal that the delivery is not just imminent, but part of a well-coordinated plan. The timeline? Soon. Very soon.
As the world watches in a mixture of horror and anticipation, one has to wonder: What does this mean for Ukraine, and for the international community at large? The stakes are as high as they’ve ever been.
The White House has made its stance crystal clear: any move by Iran to arm Russia in this manner would be met with severe repercussions. “This represents a dramatic escalation in Iran’s support for Russia’s war of aggression against Ukraine,” warned a spokesman for the U.S. National Security Council. The message is unequivocal: such actions will not go unpunished.
And yet, here we are, teetering on the edge of a new crisis, with Tehran seemingly undeterred. Iran’s official line? Denial, wrapped in the language of diplomacy. A statement from Iran’s mission to the United Nations insists that while Tehran and Moscow enjoy a strategic partnership, there has been no move to transfer these missiles to Russia for use in Ukraine. But can we take this at face value? The whisperings from intelligence circles suggest otherwise.
It’s a game of high stakes and even higher risks. With U.N. Security Council restrictions on Iran’s missile exports lifted as of October 2023, the legal barriers have crumbled, leaving Iran with a freer hand to engage in military trade. But ethical concerns remain, particularly given the devastating potential of these weapons if deployed on Ukrainian soil.
The Fath-360, with its 120-kilometer range and 150-kilogram warhead, could tilt the balance in Russia’s favor, allowing it to stretch its resources further by reserving its own missile stockpile for more distant targets. For Ukraine, already struggling to defend against Russia’s relentless assault, the introduction of these missiles would be a nightmare scenario, stretching their missile defense systems to the breaking point.
And what of the broader implications? Iran’s deepening military cooperation with Russia raises troubling questions about the future of global alliances. This isn’t just about Ukraine; it’s about the shifting sands of power in a world where old alliances are fraying and new ones are forming in ways that could have far-reaching consequences.
Let’s not forget the specter of further sanctions. The United States and European Union have maintained a firm stance on Iran’s ballistic missile program, wary of its potential to disrupt regional stability. Yet, Tehran seems unfazed, emboldened by its partnership with Moscow and perhaps, by the belief that the global community is too divided, too distracted, to mount a unified response.
As we inch closer to what feels like an inevitable showdown, the world holds its breath. Will Iran follow through with its missile deliveries? And if it does, how will the West respond? The answers could very well determine the course of the conflict in Ukraine—and beyond.
In a world increasingly defined by uncertainty and conflict, one thing is clear: the game is far from over. And as Iran and Russia continue to forge ahead with their military cooperation, the rest of the world can only watch—and wait—for the next move in this deadly game of chess.
Russia-Ukraine War
Kenyan Intelligence Report Says Over 1,000 Nationals Recruited to Fight for Russia

Promised $2,400 a month — sent to the battlefield after days of training. A new intelligence report reveals how Kenyans ended up in the Russia-Ukraine war.
More than 1,000 Kenyans have been recruited to fight on Russia’s side in the war in Ukraine, according to a classified report submitted to parliament by Kenya’s National Intelligence Service (NIS).
The report, presented Wednesday by Majority Leader Kimani Ichung’wah, describes what he called a “deeply disturbing” network of rogue officials allegedly working with human trafficking syndicates to funnel recruits into the conflict. As of February, 89 Kenyans were reportedly on the front lines. Another 35 were in military camps in Russia, 39 injured and 28 listed as missing.
Those targeted, the report says, include former military personnel, ex-police officers and unemployed men aged 20 to 50. Recruiters allegedly promised salaries of up to 350,000 Kenyan shillings ($2,400) per month, along with hefty bonuses. Instead, many found themselves deployed to combat zones after only weeks — or in some cases days — of weapons training.
“They are told you are going to work as a guard… only to get there and you are taken to military camps,” Ichung’wah told lawmakers. “They are basically just giving you a gun to go and die.”
The intelligence report outlines alleged collusion involving recruitment agencies and rogue airport staff, immigration officers, and officials from Kenya’s Directorate of Criminal Investigations. It also claims possible involvement of individuals linked to diplomatic missions, allegations the Russian embassy in Nairobi has strongly denied.
In a statement, the embassy rejected what it called “dangerous and misleading” claims and said it had never issued visas to Kenyans seeking to participate in Russia’s “Special Military Operation.” It added that while Russia does not recruit abroad, foreign nationals legally present in Russia may volunteer under Russian law.
Kenyan authorities say they have shut down more than 600 suspect recruitment agencies and are working with Moscow to curb illegal enlistment. Foreign Minister Musalia Mudavadi is expected to visit Russia next month to discuss the issue further.
So far, 27 Kenyan nationals have been repatriated, with psychological support provided upon return. Pressure is mounting on Nairobi to dismantle trafficking networks and prevent further departures, especially as reports emerge of African nationals killed in the conflict.
The revelations highlight how global wars can reach deep into vulnerable communities thousands of miles away — turning economic desperation into a pipeline to distant battlefields.
Russia-Ukraine War
Russian General Boasted of Torture and Killing of Ukrainian Prisoners

Leaked messages, graphic photos, and chilling boasts — new revelations are intensifying scrutiny over alleged abuses of Ukrainian POWs.
A decorated Russian general allegedly described acts of torture and the killing of Ukrainian prisoners of war in private messages obtained and verified by investigative journalists, raising renewed concerns over alleged war crimes in the conflict.
The messages, spanning from 2022 to 2024, were published by investigative units of Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. Journalists said the communications were sourced from within the Ukrainian military and independently verified.
The officer, identified as Roman Demurchiev, 49, reportedly shared graphic accounts of abuse against detained Ukrainian soldiers, including references to mutilation and execution. In one exchange from October 2022, he allegedly sent a photograph appearing to show severed human ears, claiming they had been taken during a three-day assault on a Ukrainian position.
In separate messages, Demurchiev appeared to discuss the fate of captured prisoners, at times suggesting they could be “disposed of” or used for forced labor. One detainee referenced in the correspondence — a volunteer from Zaporizhzhia — was later exchanged after nearly two years in captivity. Through relatives, the man said he remains psychologically unable to publicly recount his detention, though family members described severe beatings and electric shocks.
Demurchiev has previously attended high-level military meetings and received commendations, including a promotion to major general in 2023. As of late 2024, he was reported to be serving as deputy commander of Russia’s 20th Combined Arms Army. Russian authorities have not publicly responded to the allegations.
The revelations come amid mounting documentation from international observers. The United Nations Human Rights Monitoring Mission in Ukraine has reported widespread abuse of Ukrainian prisoners, stating that a vast majority of former detainees described physical or psychological torture during captivity.
Human rights groups argue the alleged conduct reflects a broader pattern rather than isolated incidents. Previous investigations have detailed claims of mistreatment, forced confessions and in some cases extrajudicial executions.
Moscow has consistently denied committing systematic war crimes in Ukraine, accusing Kyiv and Western governments of misinformation. However, the newly published messages are likely to intensify calls for further independent investigations — and potentially, accountability at the highest levels of command.
As the war grinds on, the allegations underscore a darker front in the conflict: the treatment of those captured behind the lines.
Russia-Ukraine War
Europe’s Spies Challenge Trump’s Ukraine Peace Optimism

Washington says a deal is “reasonably close.” Europe’s top spies say Moscow isn’t serious. Who’s reading the Kremlin right?
Senior European intelligence officials are casting doubt on the prospects of a Ukraine peace agreement this year, warning that Moscow has little interest in ending the war quickly — despite President Donald Trump’s claim that US-brokered diplomacy has brought a deal “reasonably close.”
The heads of five European spy agencies, speaking anonymously to Reuters, said Russia appears to be using ongoing talks with Washington as leverage to pursue sanctions relief and economic concessions rather than a genuine settlement. One intelligence chief described the latest Geneva round as “negotiation theater.”
Their assessments expose a widening gap between European capitals and the White House. Trump has expressed confidence that Russian President Vladimir Putin wants a deal, and Kyiv says Washington hopes to secure an agreement by June, ahead of US mid-term elections in November.
But European intelligence leaders see no shift in Moscow’s core objectives. “Russia is not seeking a peace agreement. They are seeking their strategic goals, and those have not changed,” one official said, pointing to demands that Ukraine abandon its Western alignment and remove President Volodymyr Zelenskyy from power.
Russia currently occupies large portions of eastern Ukraine, including most of the Donetsk region. Moscow has demanded that Kyiv withdraw from the remaining 20 percent of Donetsk still under Ukrainian control — a condition Kyiv has firmly rejected.
Even if Ukraine conceded territory, some European officials warn that such a move would likely trigger new Russian demands rather than end the conflict. One spy chief said there is a “misplaced belief” in some quarters that territorial concessions would rapidly unlock peace.
Another concern raised by European intelligence centers on parallel negotiations. Two officials said Moscow is attempting to split talks into separate tracks: one focused on ending the war and another centered on potential US-Russia economic cooperation, including relief from sanctions.
Ukrainian officials have alleged that discussions include proposals for large-scale bilateral deals worth trillions of dollars — claims the European intelligence chiefs declined to detail.
While Russia’s economy faces pressure from sanctions, high interest rates and shrinking fiscal reserves, European analysts describe it as resilient enough to sustain prolonged conflict. The country’s central bank rate remains elevated, and access to global capital markets is restricted, but Moscow has adapted to wartime conditions.
The White House dismissed the anonymous criticism, with a spokesperson saying President Trump and his team have done more than anyone to bring both sides together.
For now, diplomacy continues. But across Europe’s intelligence community, skepticism runs deep: without a fundamental shift in Moscow’s objectives, they see little chance that 2026 will deliver the breakthrough Washington is seeking.
Russia-Ukraine War
Estonia Warns NATO Would Strike Deep Inside Russia if Baltics Are Invaded

If Moscow moves on the Baltics, Estonia says the fight won’t stop at the border — it will go deep into Russia.
NATO would launch strikes “very far into Russia” if Moscow dares to invade the Baltic states, Estonia’s foreign minister has warned, dismissing fears that the Kremlin could quickly seize territory in Eastern Europe.
Speaking on the sidelines of the Munich Security Conference, Estonian Foreign Minister Margus Tsahkna said Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania would not wait passively for reinforcements if Russian forces crossed their borders.
“We’ll bring the war to Russia,” Tsahkna said, arguing that Baltic defense planning has shifted from relying solely on NATO’s eventual victory to immediate counteraction. “We cannot let Russia into the Baltic States and then fight back.”
His remarks come amid growing concern that President Vladimir Putin could test NATO’s resolve after the war in Ukraine, potentially by targeting one of the alliance’s smaller eastern members. Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania — all NATO members — border Russia and are viewed as particularly exposed.
Recent war-game simulations have fueled anxiety. One high-profile scenario envisioned Russia rapidly invading Lithuania and securing key objectives within days, including control of the strategically vital Suwalki Gap — the narrow corridor linking the Baltics to the rest of NATO territory. Another potential flashpoint often cited is Narva, an Estonian border town with a large Russian-speaking population.
But Tsahkna rejected such scenarios as outdated and overly pessimistic, arguing that Baltic defense capabilities have been significantly strengthened. He pointed to a surge in military spending across the region, with Baltic governments committing up to 5 percent of GDP to defense — well above NATO’s 2 percent benchmark.
The message from Tallinn reflects a broader shift in NATO’s eastern flank strategy. Rather than planning to reclaim territory after an invasion, Baltic leaders now emphasize forward defense and immediate retaliation to deter aggression in the first place.
While NATO’s collective defense clause — Article 5 — remains the alliance’s cornerstone, debate continues over how quickly and decisively members would respond in a real crisis. For Estonia, the answer, at least rhetorically, is clear: any invasion would trigger not just defense, but deep strikes inside Russia itself.
Russia-Ukraine War
China Pledges Help to Kyiv While Washington Says It Fuels Moscow

Beijing offers energy support to Ukraine — but buys record volumes of Russian oil. Diplomacy or double game?
China has pledged new humanitarian energy assistance to Ukraine, even as U.S. officials publicly accused Beijing of enabling Russia’s war effort.
Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi met Ukrainian Foreign Minister Andrii Sybiha on the sidelines of the Munich Security Conference, where he offered support to help Ukraine repair energy infrastructure repeatedly targeted by Russian missile and drone strikes. Kyiv welcomed the additional assistance, though China has not disclosed the size or scope of the package.
At the same conference, U.S. Ambassador to NATO Matthew Whitaker delivered a pointed rebuke. He said China has the leverage to end the conflict by cutting off “dual-use technologies” supplied to Moscow and halting purchases of Russian oil and gas.
“This war is being completely enabled by China,” Whitaker said.
Beijing denies supplying lethal military aid to Russia and maintains it is not a party to the conflict. Chinese officials say they support dialogue and a political settlement. Yet Western governments increasingly view China as Russia’s most important external economic partner.
Trade between Beijing and Moscow has expanded sharply since the 2022 invasion. China is again the largest buyer of Russian crude, with tracking data showing approximately 1.65 million barrels per day delivered to Chinese ports in January — near post-invasion highs. Those purchases provide critical revenue for the Kremlin as Western sanctions attempt to restrict Moscow’s war financing.
The juxtaposition is striking: China offering humanitarian energy aid to Ukraine while deepening commercial ties with Russia. For European governments considering additional measures against Chinese firms accused of supplying dual-use components, Beijing’s outreach to Kyiv complicates the diplomatic landscape.
For Washington, the message in Munich was clear. China’s economic and technological weight gives it the power to influence Russia’s trajectory — and U.S. officials argue that Beijing has chosen not to use that leverage.
Middle East
Separate U.S. Talks on Iran and Ukraine-Russia Set for Tuesday in Geneva

One city. Two crises. U.S. envoys head to Geneva for high-stakes talks on Iran and the Ukraine war.
Two separate rounds of high-level diplomacy — focused on Iran and the war in Ukraine — are scheduled to take place Tuesday in Geneva, according to a source briefed on the matter.
A U.S. delegation that includes special envoys Steve Witkoff and Jared Kushner is expected to meet Iranian representatives in the morning session. Officials from Oman will mediate the discussions, continuing Muscat’s role as an intermediary between Washington and Tehran.
The talks come as President Donald Trump intensifies pressure on Iran following its crackdown on domestic protests and amid an expanded U.S. naval presence in the region.
Later in the day, Witkoff and Kushner are scheduled to join trilateral negotiations involving representatives from Russia and Ukraine. The discussions are part of ongoing efforts to explore potential pathways toward ending Russia’s four-year invasion of Ukraine.
While the two diplomatic tracks are separate, their convergence in Geneva underscores the breadth of U.S. foreign policy engagement at a moment of heightened global tension.
Neither the White House nor the governments involved have publicly detailed the scope or expected outcomes of the meetings. However, the simultaneous talks highlight Washington’s attempt to manage two major geopolitical crises through parallel diplomatic channels.
Russia-Ukraine War
NATO Moves North but Keeps Eyes on Ukraine
Russia-Ukraine War
Russian Strikes Leave Kyiv, Odesa and Dnipro in Darkness
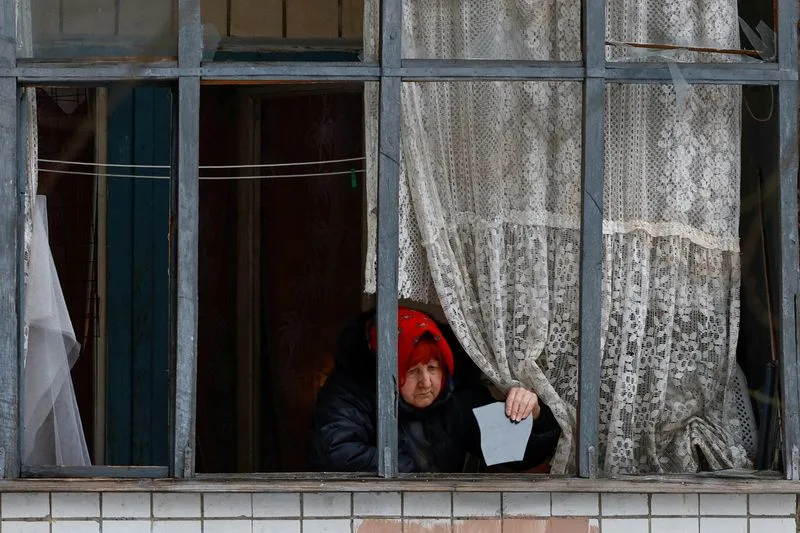

Missiles by night. Freezing apartments by morning. Ukraine’s cities face another winter blackout as diplomacy stalls.
Russia launched a sweeping overnight assault of drones and ballistic missiles on Ukraine early Thursday, knocking out power, heating and water supplies to tens of thousands of civilians in Kyiv and other major cities, Ukrainian officials said.
The barrage, which included 24 ballistic missiles, one cruise missile and 219 drones, marked the latest escalation in Moscow’s winter campaign against Ukraine’s energy grid. Ukraine’s air force said its defenses intercepted or neutralized 16 missiles and 197 drones, but significant damage was still reported.
In Kyiv, Mayor Vitali Klitschko said about 3,500 apartment buildings were without heating, including nearly 2,600 high-rises newly affected by the strike. More than 100,000 families lost electricity, according to private energy provider DTEK, which said one of its thermal power plants had been targeted. Two people were injured in the capital, and a residential building sustained damage.
The southern port city of Odesa also suffered heavy disruption. Deputy Prime Minister Oleksiy Kuleba said nearly 300,000 residents were left without water after electricity supplies were cut. Close to 200 buildings were without heating. Regional officials reported damage to an apartment block and a market fire that injured at least one person.
In Dnipro, a combined missile and drone strike wounded four people, including a baby and a four-year-old child, according to regional authorities. Elsewhere, prosecutors said two people were killed and six injured in an attack on Lozova, a railway hub in the northeastern Kharkiv region.
Moscow has repeatedly denied deliberately targeting civilians, despite widespread destruction of residential infrastructure since its full-scale invasion in 2022. Kyiv acknowledges striking targets inside Russia and Russian-occupied areas, though at a far smaller scale.
Ukraine’s Foreign Minister, Andrii Sybiha, condemned the latest assault as a setback to diplomatic efforts aimed at ending the nearly four-year war. U.S.-backed talks have yet to bridge core disagreements, even as Russian forces press offensives on the battlefield.
President Volodymyr Zelenskyy said this week that stronger international pressure on Moscow would be essential if hopes for a summer ceasefire are to materialize.
For many Ukrainians, however, diplomacy feels distant. As temperatures plunge, survival once again hinges on generators, blankets and the fragile resilience of a battered power grid.
-

 Somaliland1 month ago
Somaliland1 month agoF-35s Over Hargeisa: The Night Somaliland’s Sovereignty Went Supersonic
-

 Somalia1 month ago
Somalia1 month agoAid Destroyed, Trust Shattered: Somalia Loses U.S. Support for Good
-

 Terrorism1 month ago
Terrorism1 month agoForeign ISIS Pipeline Exposed: Puntland Captures Dozens of Non-Somali Fighters
-

 Somaliland1 month ago
Somaliland1 month agoSomaliland at Davos: The Moment Somaliland Entered the World’s Inner Circle
-

 Terrorism1 month ago
Terrorism1 month agoAmerica Pulls Back From Somalia but Doubles Down Next Door
-

 Top stories2 months ago
Top stories2 months agoSomali Pirates Hijack Chinese Fishing Vessel off Puntland Coast
-

 Middle East2 months ago
Middle East2 months agoUS War Plans Against Iran Enter Advanced Stage
-

 Analysis2 months ago
Analysis2 months agoWhy Putin Is Silent on Maduro’s Abduction—and the Limits of Putin’s Power