Analysis
Somaliland’s Geopolitical Dilemmas and Security Risks Amid Potential Gaza Resettlement Plans

Somaliland faces a complex and precarious situation as it navigates potential involvement in resettling displaced Palestinians from Gaza—a proposal that could reshape its international relations and domestic stability. This scenario poses significant geopolitical and security challenges, highlighting Somaliland’s ongoing struggle for international recognition juxtaposed against maintaining its standing within the Arab and African communities.
Somaliland’s consideration of Gaza resettlement options is likely influenced by its pursuit of international recognition, particularly from major powers like the USA and potential allies like Israel. Engaging in such discussions could indeed position Somaliland favorably on an international stage, possibly opening doors to new diplomatic and economic opportunities. However, this move risks alienating key Arab and African nations that have historically supported Somaliland’s bid for sovereignty, given their general stance on the Palestinian issue.
The Arab League’s probable adverse reaction could stem from a perceived betrayal of the Palestinian cause, a sensitive and pivotal issue across Arab states. This could lead to a reduction in diplomatic and economic support from these countries, crucial for Somaliland’s economic stability and international standing. Furthermore, aligning with a plan that involves relocating Palestinians might be viewed unfavorably by other international bodies and could complicate Somaliland’s relationships within the United Nations framework, where Arab states hold significant influence.
The proposal also introduces potential security risks. By taking a central role in such a controversial plan, Somaliland could become a target for extremist groups who oppose Western interventions in Palestinian affairs. This could exacerbate internal security issues and lead to increased terrorist activity within its borders, particularly from groups like Al-Shabaab, who might extend their operations into Somaliland if it aligns too closely with Western or Israeli interests.
Moreover, the resettlement discussions could stir domestic unrest, given the sensitive nature of the Palestinian issue among the Somaliland population, which might view any participation in the resettlement as compromising the Palestinian right to their homeland. This internal dissent could lead to protests or more severe political backlash, destabilizing the internal security and harmony that Somaliland has managed to maintain despite regional conflicts.
Strategic Recommendations
For Somaliland, the way forward requires a delicate balance between advancing its international recognition and maintaining regional relationships and internal stability:
Somaliland should strengthen diplomatic ties with both Western and Arab nations without fully committing to any resettlement plans. This involves diplomatic discussions that explore the benefits of recognition while addressing the concerns of its traditional allies.
Clear communication with both its citizens and international partners about the nature and scope of any discussions related to Gaza resettlement could mitigate misunderstandings and potential backlash.
Engaging in multilateral platforms that include African and Arab mediators could help manage the diplomatic risks associated with these discussions. This approach might also facilitate broader support for Somaliland’s strategic interests.
By staying neutral on contentious international issues, Somaliland could avoid the pitfalls of geopolitical entanglements that do not directly benefit its quest for recognition or contribute positively to its regional standing.
In conclusion, while the potential involvement in Gaza resettlement could offer Somaliland an opportunity to showcase its capability and willingness to engage in international humanitarian efforts, it must carefully consider the long-term geopolitical and security repercussions. The priority should remain on achieving international recognition through strategic diplomacy that respects its historical ties and seeks to maintain regional stability and internal security.
Analysis
How One U.S. Interview Sparked a Regional Storm
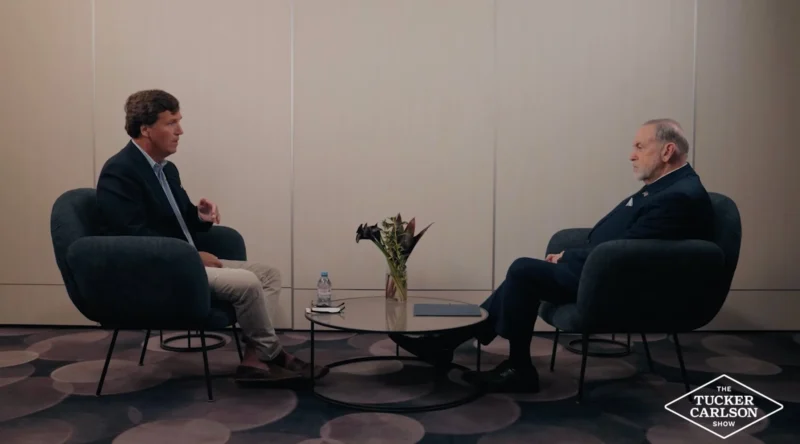

A podcast conversation in Washington has triggered diplomatic protests across the Middle East. Why did it hit such a nerve?
A recent interview between commentator Tucker Carlson and U.S. Ambassador to Israel Mike Huckabee has reverberated far beyond American media circles, prompting formal objections from more than a dozen Middle Eastern governments and reopening debate about how religious ideas shape U.S. policy toward Israel.
At the heart of the controversy were remarks interpreted as endorsing expansive biblical claims tied to the concept of a Land of Israel stretching from the Nile to the Euphrates. While supporters described the conversation as calm and substantive — a rare example of civil dialogue on polarizing issues — critics in the region viewed the comments as politically charged and destabilizing.
Foreign ministries from countries including the United Arab Emirates, Egypt, Jordan, Saudi Arabia and Qatar issued a joint condemnation, calling the remarks “dangerous and inflammatory” and warning they violated international law and threatened regional stability. Several of those governments maintain diplomatic ties with both Washington and Israel, underscoring the sensitivity of the issue.
The reaction reflects deeper anxieties. For decades, U.S. policy has rested on a framework balancing support for Israel’s security with commitments to a negotiated two-state solution. Public references to biblical claims — particularly when voiced by a senior diplomat — risk blurring the line between religious conviction and official policy.
The interview also touched on civilian casualties in Gaza and the reliability of data from the Hamas-run health ministry, raising broader questions about accountability and independent verification in conflict zones.
Yet the debate extends beyond a single podcast. Within parts of the American conservative and evangelical community, the Gaza war has sparked renewed discussion about Christian Zionism and the theological roots of support for Israel. That internal U.S. debate is increasingly visible abroad.
Regional observers note that nationalist narratives rooted in history and faith are not unique to Israel. Turkish, Arab and Kurdish political movements have all invoked expansive historical claims at various points. But in a region marked by overlapping borders and unresolved conflicts, such rhetoric can inflame tensions quickly.
Whether the Carlson-Huckabee exchange represents a shift in U.S. policy or simply personal expression remains unclear. What is certain is that Middle Eastern governments are listening closely — and responding swiftly — whenever American officials appear to redraw the map, even rhetorically.
In today’s volatile climate, words spoken in a studio thousands of miles away can ripple through capitals across the region.
Analysis
When Allies Doubt Each Other, Deterrence Fails

Analysis: NATO’s Ability to Deter Russia Has Taken a Hit.
For most of its history, NATO’s strength rested less on troop numbers than on credibility—the shared belief that an attack on one would trigger a response from all. That credibility, analysts now warn, has been quietly eroding, not because Europe is unwilling to spend on defense, but because trust inside the alliance has frayed.
European allies and Canada are pouring unprecedented resources into military budgets and into Ukraine’s war effort. Yet deterrence depends on perception, and recent trans-Atlantic infighting has punctured the image of NATO as a unified force under U.S. leadership.
The most damaging rupture came not on the battlefield but in rhetoric. U.S. President Donald Trump’s repeated threats to seize Greenland—a semiautonomous territory of NATO member Denmark—crossed a psychological line for allies. Even without force, the suggestion that one ally might coerce another undermines the alliance’s core principle: that members’ borders are inviolable.
That principle is embedded in Article 5, NATO’s collective-defense clause. While Article 5 does not apply to internal disputes, its power lies in the assumption that allies will never threaten one another in the first place. Once that assumption cracks, so does deterrence.
European unease deepened after Trump’s disparaging remarks about allied troops who fought alongside U.S. forces in Afghanistan. Though partially walked back, the comments reinforced an old fear: that Washington’s commitment is conditional, transactional, and ultimately unpredictable.
From Moscow’s perspective, this uncertainty is an opportunity. Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov has openly noted the upheaval inside NATO, while Russian state media mock what they describe as Europe’s “impotent rage.” The message is clear: deterrence weakens when resolve looks divided.
To counter U.S. criticism over burden-sharing, NATO allies agreed last year to dramatically raise defense spending, pledging up to 5% of GDP over time when security-related investments are included. NATO Secretary-General Mark Rutte has framed this as proof of the alliance’s renewed strength. But spending, however necessary, cannot substitute for political cohesion.
The danger lies not in an immediate Russian assault, but in gradual erosion. Deterrence fails not all at once, but through probing—cyberattacks, sabotage, intimidation, and gray-zone operations that test whether NATO will respond decisively. European officials already report mysterious drone flights, infrastructure sabotage, and information warfare across the continent.
For Russian President Vladimir Putin, the calculation is straightforward: if NATO members doubt each other, escalation becomes less risky. As EU officials warn, Russia is not deterred by declarations alone, but by the belief that unity will hold under pressure.
The unresolved question is the U.S. military footprint in Europe. American troops remain central to NATO’s deterrence posture, yet uncertainty over future deployments—especially after partial withdrawals near Ukraine—has amplified doubts. Even if U.S. forces do not leave en masse, ambiguity itself weakens the deterrence equation.
NATO is not collapsing. Its military capacity is growing, and its members still share core interests. But credibility is fragile. Once allies begin to wonder whether commitments are real—or whether allies might turn on one another—the deterrence edifice becomes shakier.
For Europe, the lesson is stark. Rearmament is necessary, but it is not enough. Deterrence depends on unity, predictability, and restraint among allies themselves. When those erode, adversaries do not need to attack. They simply wait—and watch.
Analysis
How Grounded Flights Exposed Somalia’s Electoral Fault Lines

Flights Turned Back, Trust Grounded: Why the Puntland–Jubaland Incident Matters for Somalia’s 2026 Elections.
A Small Incident With Big Political Consequences.
At first glance, the decision to turn back two flights bound for Mogadishu may appear like a technical dispute over landing clearances. In reality, the incident has exposed a far deeper crisis in Somalia’s fragile political process—one that goes to the heart of trust, security guarantees, and the credibility of the country’s path toward elections in 2026.
On Sunday, advance delegations from Puntland and Jubaland were ordered to return to Garowe and Kismayo just minutes before landing at Aden Adde International Airport. The timing could not have been more sensitive. February 1 was the date originally scheduled for a national consultative forum intended to lay the groundwork for Somalia’s next electoral process.
The reaction from international partners was unusually direct. The European Union, through its ambassador Francesca Di Mauro, publicly expressed regret and urged Somali leaders to find a solution that would allow the dialogue to proceed. The United Nations mission in Somalia, United Nations, echoed those concerns, stressing the need to prioritize dialogue as constitutional mandates near their end.
That convergence of EU and UN messaging matters. It signals that the incident is not being treated as a routine administrative mishap, but as a political warning sign.
Security or Control?
The federal government’s explanation, delivered by Defence Minister Ahmed Macalin Fiqi, was that Puntland and Jubaland were attempting to bring excessive armed personnel and weapons into Mogadishu. Both regional administrations categorically rejected the accusation, insisting that only standard presidential security details and staff were on board.
This dispute highlights a central dilemma in Somalia’s federal system. Regional leaders do not trust Mogadishu to guarantee their safety without their own security details. Mogadishu, in turn, views those same details as a challenge to its authority over the capital. The result is a zero-sum security logic that turns even routine political travel into a high-risk confrontation.
When Puntland President Said Abdullahi Deni labeled the incident a “criminal act,” he was not just speaking about aviation safety. He was framing the episode as evidence that the federal government cannot be trusted to act as a neutral convener.
The Cost to the Electoral Process
The immediate casualty of the incident is the national consultative forum itself. Technical committees had spent weeks preparing the agenda alongside the Federal Government and political stakeholders. That work is now overshadowed by a more basic question: can Somali leaders even gather in the same room under mutually accepted conditions?
Elections require more than laws and timelines. They require confidence that participation will not be punished, manipulated, or physically endangered. Turning back delegations—especially on the day talks were due to begin—undermines that confidence in a way that is difficult to repair quickly.
The fact that Jubaland also reported civilian flights being denied landing permission deepens the concern. Whether intentional or not, the optics suggest collective punishment and politicization of airspace, a dangerous precedent in a country where mobility is already constrained by insecurity.
Why This Moment Matters
Somalia is approaching a convergence of deadlines: expiring mandates, contested electoral models, and growing polarization between Mogadishu and key federal member states. Against that backdrop, inclusivity is not a slogan—it is a requirement.
By grounding planes instead of guaranteeing safe passage, Somali politics has sent the opposite signal. International partners have noticed. So have domestic actors.
What makes this episode especially damaging is not that talks were delayed, but that trust was publicly broken. Rebuilding that trust will require more than statements. It will require clear, enforceable guarantees that all stakeholders—federal and regional—can participate in national processes without fear or humiliation.
In Somalia’s long political journey, crises often emerge not from grand confrontations, but from seemingly small acts that reveal deeper intentions. This was one of those moments. The planes turned back, but the larger risk is that dialogue itself may now struggle to take off.
Analysis
How Chinese Speculators Set the Stage for the Gold and Silver Crash

How Chinese Speculation Fueled — and Then Crashed — the Global Gold and Silver Rally.
For decades, gold has been treated as the ultimate financial anchor — slow-moving, liquid, and immune to sudden shocks. Silver, though more volatile, rarely strays far from its industrial fundamentals. That illusion shattered last week, when both metals collapsed at a speed that stunned even veteran traders.
Silver fell more than a quarter in a single day, the largest drop on record. Gold lost nearly a tenth of its value in hours, its worst performance in more than ten years. The crash did not begin with mine supply, industrial demand, or central-bank policy. It began with speculation — and it began in China.
For weeks, metals markets had been behaving less like commodity exchanges and more like momentum-driven casinos. Prices for gold, silver, copper, and tin surged in near-vertical lines, defying traditional valuation models. Traders in Europe and the United States stopped sleeping through Asian hours, knowing that the biggest moves were coming while Shanghai was open.
What changed was not the fundamentals. It was the flow of money.
A wave of speculative capital from China — ranging from retail investors to equity funds branching into commodities — flooded into metals markets. Gold became a proxy bet against the dollar. Silver became a leverage play. Copper turned into a macro hedge. Trend-following funds amplified the move, chasing prices higher simply because they were rising.
At that point, the rally ceased to be about inflation, geopolitics, or supply constraints. It became mechanical.
Options activity exploded, particularly in silver. Call options piled up at a scale rarely seen outside equity bubbles. That created a self-reinforcing loop: as prices rose, dealers were forced to hedge by buying more metal, which pushed prices higher still. The result was a classic squeeze — violent on the way up, and unforgiving on the way down.
The spark that reversed the trade came from Washington, not Beijing. News that President Donald Trump planned to nominate Kevin Warsh as Federal Reserve chair strengthened the dollar and punctured the belief that US monetary policy would remain indefinitely loose. Gold cracked within minutes. Once the Asian session opened, Chinese investors did something that Western traders had been waiting for but still feared: they took profits.
The selling did not look panicked. It was decisive.
Once momentum broke, liquidity vanished. Markets that had looked deep and orderly suddenly felt “untradeable,” as one strategist put it. Silver’s size worked against it. With an annual market value far smaller than gold’s, even modest outflows translated into extreme price swings. ETFs that once traded quietly suddenly became some of the most active securities on the planet — a sign not of confidence, but of stress.
The episode exposed a structural truth about modern commodities markets. In an era of cross-border capital flows, derivatives, and retail speculation, price discovery can detach from physical reality far faster than in the past. Gold may still symbolize stability, but its price no longer guarantees it.
What happens next will again depend on China. Domestic exchanges impose daily price limits, meaning much of the adjustment may still be ahead. Ahead of the Lunar New Year — traditionally a peak buying season — Chinese banks have already moved to curb retail exposure, tightening deposits and imposing quotas. That alone suggests policymakers see risk where investors recently saw opportunity.
There may yet be dip buyers, particularly in physical gold. Silver, however, appears to have lost its spell. For now, traders are no longer asking how high metals can go. They are asking a more sobering question: how much of the rally was ever real to begin with.
The crash was not an accident. It was the inevitable end of a trade driven less by belief than by momentum — and momentum, once broken, has no loyalty.
Analysis
Iran Warns, Qatar Mediates, Washington Deploys: A Crisis Managed in Public and Private

U.S. Warships, Quiet Talks: Why Washington and Tehran Are Signaling Force and Diplomacy at the Same Time.
The deployment of a U.S. naval strike group led by the aircraft carrier USS Abraham Lincoln off Iran’s coast is not a prelude to immediate war. It is a reminder of leverage. At the same time President Donald Trump publicly claims that Iran is “negotiating,” Tehran’s military leadership warns of retaliation, and regional mediators quietly move between capitals. Together, these signals point to a familiar but volatile pattern: coercive diplomacy.
Trump’s comments reveal a deliberate ambiguity. By asserting that talks are underway while refusing to outline military plans—even to allies—he keeps pressure squarely on Tehran. The message is simple: negotiations remain possible, but the alternative is visible and credible force. The carrier strike group is not there to fight tomorrow; it is there to shape decisions today.
From Washington’s perspective, timing matters. Iran has just emerged from weeks of nationwide unrest marked by lethal repression. Intelligence assessments suggest the regime is under strain—economically brittle, politically defensive, and wary of further escalation. That context explains why U.S. officials believe Iran may prefer negotiation to confrontation, even as its generals issue warnings meant to deter attack and reassure domestic audiences.
Iran’s response follows a well-worn script. Senior commanders insist that nuclear knowledge “cannot be eliminated” and warn that any strike would endanger regional security, including Israel’s. These statements serve two purposes. Externally, they aim to raise the perceived cost of U.S. or Israeli action. Internally, they project strength at a moment when the state’s legitimacy has been shaken by protests and competing casualty narratives.
The presence of Qatar’s foreign minister in Tehran adds a critical layer. Doha has become one of the region’s most active intermediaries, trusted enough by Washington and Tehran to carry messages neither side wants to deliver directly. Qatar’s push for de-escalation does not contradict U.S. force deployment; it complements it. Pressure creates urgency. Mediation offers an exit.
Crucially, neither side appears to want uncontrolled escalation. The United States has framed its demands narrowly: limits on nuclear and missile programs and restraint in regional behavior. Iran, while signaling openness to nuclear talks, draws a firm line around missiles and defense—core pillars of regime security. This gap defines the negotiation space and the risk zone.
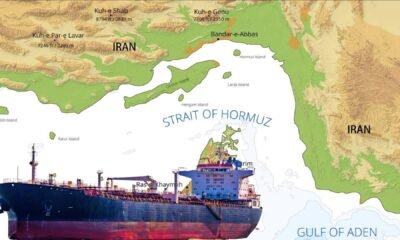
The Strait of Hormuz looms over all of it. Any clash there would ripple through global energy markets and regional stability. CENTCOM’s warning to the IRGC against unsafe naval behavior underscores how easily miscalculation could turn signaling into confrontation. Exercises, patrols, and shadowing operations are as much about discipline as dominance.
The protests themselves, though currently subdued, remain part of the equation. Washington has openly linked its posture to Tehran’s crackdown, while Iranian authorities frame unrest as foreign-backed subversion. That mutual suspicion limits trust but also reinforces caution: both sides know escalation could inflame internal pressures they cannot fully control.
What emerges is not a march toward war, but a standoff calibrated to avoid it—so long as talks show signs of movement. The carrier group, the warnings, the mediation, and the rhetoric are all tools in a single strategy: force first to compel seriousness, diplomacy second to channel it.
Whether that balance holds depends on restraint at sea, discipline in rhetoric, and the willingness of both sides to test compromise without appearing weak. For now, the crisis is being managed, not resolved. The fleet offshore is the reminder of what happens if management fails.
Analysis
Europe’s IRGC Move Sends a Message but Needs Muscle

From Label to Leverage: What the EU’s IRGC Terror Designation Can and Cannot Achieve.
When the European Union formally designated Iran’s Revolutionary Guards as a terrorist organization, it broke with years of hesitation and internal legal wrangling. The move carries weight. It freezes assets, criminalizes support networks and signals that Europe now views the Guards not as a conventional state institution but as a driver of transnational violence and repression.
Yet the practical question begins where the symbolism ends. A label changes the legal environment, but it does not by itself change the political reality inside Iran.
The IRGC is not a peripheral militia. It is embedded in the country’s security services, economy and regional strategy. Any effort to weaken its influence therefore intersects with the daily lives of ordinary Iranians, the structure of the state and the balance of power across the Middle East. Treating the designation as a magic switch for regime change risks misunderstanding how resilient and adaptive the Iranian system has proven to be over decades of pressure.
The most immediate effect will likely be financial and operational. European banks and companies will move to further distance themselves from entities linked to the Guards. That can complicate the funding and logistics of IRGC-connected networks in places like Syria and Lebanon. It also tightens the legal net around procurement and technology flows that might otherwise pass quietly through European jurisdictions.
But sanctions and listings historically work as slow constrictors, not instant breakers. They raise costs and narrow options; they do not automatically produce collapse. Inside Iran, the Guards have repeatedly shown an ability to shift resources, reroute trade and deepen their hold over parts of the domestic economy when external pressure rises.
The EU’s decision also lands in a volatile domestic context. Iran has faced waves of protest driven by economic strain, social frustration and anger at repression. External actors must tread carefully. Overt attempts to choreograph internal resistance from abroad can delegitimize local movements in the eyes of parts of the population and give authorities a ready narrative of foreign orchestration.
If Europe wants its designation to amount to statecraft rather than symbolism, the next steps are likely to be less dramatic but more durable. One track is governance of the gray zones that allow sanctioned actors to keep operating. That means tighter export controls on dual-use goods, closer intelligence cooperation on illicit finance and consistent enforcement across member states so that loopholes do not simply migrate from one capital to another.
Another track is people-focused rather than regime-focused. Expanding channels for academic exchange, visas for at-risk activists, and independent media support can widen Iranian society’s exposure to alternatives without prescribing a political outcome. Protecting the digital space through stronger cybersecurity cooperation and resilience against internet shutdowns can also make it harder for any authority to monopolize information.
There is also a regional dimension. The Guards’ influence extends through partnerships and proxies across the Levant and the Gulf. Coordinated maritime security, air defense integration among regional states and de-escalation mechanisms can blunt the spillover risk if tensions rise, without turning every confrontation into a binary showdown.
Perhaps most important is clarity about ends and means. If the objective is to reduce the Guards’ capacity for repression and external militancy, then measures that chip away at their revenue streams, procurement networks and freedom of movement are coherent. If the objective is regime collapse, then Europe is entering terrain where it has limited leverage and high uncertainty over what follows.
History offers a caution. Sudden state breakdowns without agreed transition paths can produce power vacuums that invite fragmentation or new forms of coercion. Any serious conversation about Iran’s future therefore has to include engagement with a broad spectrum of Iranian civil society and opposition voices, not just pressure on the institutions of power.
The EU’s designation is consequential. It redraws legal lines and alters calculations for anyone doing business at the edges of the Guards’ vast network. But it is the beginning of a policy chapter, not its conclusion. Turning symbolism into strategy will depend less on dramatic gestures than on patient, coordinated work that constrains violence, protects society and keeps channels open for a future that Iranians themselves ultimately determine.
Analysis
Surprise in Jerusalem as Ankara Dangles Conditional Normalization

Turkey Signals Conditional Restoration of Trade With Israel, Catching Jerusalem Off Guard.
Jerusalem’s surprise at Turkey’s talk of restoring trade is less about the content of the message than the timing and messenger. For years, the Turkey–Israel relationship has been defined by a paradox: harsh public hostility alongside pragmatic back-channel coordination. Ankara’s latest signal adds a new twist by suggesting that the rupture is reversible, but only after the Gaza war ends and humanitarian access improves.
That framing matters. By calling the break “conditional rather than structural,” Turkish Foreign Minister Hakan Fidan is saying the problem is policy, not existence. In practical terms, Ankara is leaving the door ajar for normalization without abandoning its domestic narrative of standing firmly with Palestinians. It is an attempt to square two audiences at once: a Turkish public steeped in anti-Israel rhetoric and an international arena where Turkey seeks relevance in Gaza’s postwar order.
For Israeli officials, the difficulty is deciding whether this is a genuine pivot or a tactical maneuver. Mistrust runs deep. President Recep Tayyip Erdogan’s rhetoric, amplified by state-aligned media, has repeatedly crossed lines that make easy reconciliation politically toxic in Israel. The absence of ambassadors and the need to station Israeli diplomats outside Turkey underline how abnormal relations have become.
Yet Israel has never treated Turkey as an outright adversary. Security channels have stayed alive, and both sides understand the value of limited coordination in a volatile region. That is why Fidan’s language, while abrasive in its criticism of Israel’s conduct in Gaza, still resonates in Jerusalem as potentially workable. If the rupture is truly conditional, then a pathway back exists.
The immediate catalyst is Gaza’s uncertain endgame. Washington is pushing for arrangements that would stabilize and rebuild the enclave once fighting stops. Turkey wants a seat at that table. Ankara’s recent role in hostage diplomacy impressed the White House, and U.S. planners see Turkish construction and logistics capacity as useful for reconstruction. Israeli objections to Turkish troops in any stabilization force are firm, but blocking Turkish companies from rebuilding is far less likely. Trade, not boots, could become the bridge.
This is where Ankara’s signal begins to look strategic. By tying trade restoration to the war’s end and humanitarian access, Turkey positions itself as both critic and future partner. It lowers diplomatic friction with Jerusalem just enough to make Turkish participation in Gaza projects politically feasible in Washington. At the same time, it preserves leverage by keeping normalization contingent on Israeli behavior.
Israel’s unease is also shaped by Turkey’s moves beyond Gaza. Ankara’s military footprint in northern Syria, its campaign against Kurdish forces, and reports of support for Syria’s current leadership raise alarms in Jerusalem about Turkish air and ground capabilities close to Israel’s northern approaches. Add to that Turkey’s mediation between Washington and Tehran and Fidan’s claim that Israel is pressing for U.S. military action against Iran, and the trust deficit widens further.
Still, both capitals recognize the relationship is not irreparable. A limited thaw could begin with practical steps that avoid symbolism. Resuming trade flows would test intentions without requiring dramatic gestures. The return of Turkish Airlines to Tel Aviv would signal normalcy, though the market has largely adjusted with Gulf carriers filling the gap. Quiet restoration of consular presence could follow, long before ambassadors return.
The obstacles are real. Turkish public discourse remains severe, and Israeli politics offers little appetite for rapprochement while Gaza remains unresolved. But the logic of conditionality creates space for incrementalism. It allows Ankara to claim principle and Jerusalem to claim pragmatism.
In the near term, a full reset is unlikely. What is plausible is a transactional easing driven by U.S. priorities for Gaza’s postwar phase. If the guns fall silent and aid moves freely, Ankara can argue that its conditions have been met. Jerusalem, wary but realistic, may accept a narrow opening that serves reconstruction without conceding on security.
The surprise in Jerusalem reflects how unusual it is to hear conciliatory subtext from Ankara amid hostile headlines. Whether that subtext becomes policy will depend less on speeches than on events in Gaza. If the war ends and reconstruction begins, Turkey is signaling it wants back in the room. Israel’s response will determine whether that room has a door.
Analysis
Why Somaliland Now Sits at the Center of Global Strategy

Ports, Power, and the Red Sea: Why Somaliland Now Sits at the Center of Global Strategy.
Somaliland sits beside the Bab el-Mandeb, a maritime chokepoint so critical that its geography transcends regional relevance and becomes a lever of global power. In today’s geopolitical climate, the Red Sea is rapidly evolving into a corridor of coercion, where the ability to keep transit open determines the flow of trade, energy, and strategic timelines. This is not a localized contest but a global one, and the absence of sustained Western engagement is quietly opening space for revisionist powers to shape the rules.
China, Russia, and Turkey are steadily expanding their footprint across the Horn of Africa, converting presence into basing options and diplomatic gravity. Their method is not built on democratic persuasion but on structural entanglement: ports that double as political leverage, security dependencies that translate into elite patronage networks, and narratives that rebrand coercion as partnership.
The challenge they pose to the West is blunt—either compete for these chokepoints or consent to being governed by them.
For too long, Western policy has treated Somaliland as a diplomatic anomaly rather than what serious strategists recognize: essential terrain. International recognition remains trapped in procedural inertia, but on the ground Somaliland operates as a functioning, secure polity. In contrast to Somalia’s ongoing struggle with terrorism, Somaliland has cultivated internal stability capable of supporting durable partnerships.
That stability carries regional consequences. It offers Ethiopia—landlocked, rapidly growing, and precariously dependent on Djibouti—a critical outlet through the Berbera corridor, reducing the vulnerability of a national economy exposed to chokepoint politics.
Here lies a rare strategic opening for the United States. Somaliland has signaled, through institutional development and a market-oriented outlook, that it is prepared to integrate into a rules-based trade and security architecture. U.S. recognition should be understood not as diplomatic charity but as strategic alignment with the entity that actually governs and secures the territory.
Prolonged ambiguity does not preserve neutrality; it rewards adversaries who entrench influence without waiting for perfect paperwork.
That alignment is further reinforced by an emerging convergence between Somaliland, the United Arab Emirates, and Israel. Each contributes a distinct pillar to regional stability: Somaliland supplies the geography and resource potential; the UAE brings capital and logistical sophistication; Israel offers security innovation and technological expertise in water and agriculture—capabilities essential for sustaining a desert economy. Together, they raise the operational costs for any hostile actor seeking to manipulate the Red Sea corridor.
Taiwan’s engagement adds another revealing dimension. By bypassing traditional diplomatic constraints, Taipei has helped build Somaliland’s digital and health infrastructure, demonstrating that in contested environments, influence flows most durably from those who expand tangible state capacity. It is a model of functional diplomacy adapted to a competitive era.
Ultimately, the traditional diplomatic map is being replaced by one defined by logistics and infrastructure. The United States must move beyond viewing the Horn of Africa as a zone of episodic crisis and recognize it as a primary theater of strategic competition. That means deepening maritime security cooperation, backing transparent investment frameworks, and accepting a simple reality: if the West remains absent, the Red Sea corridor will not stay neutral. It will become hostile by default.
Power today speaks through ports and corridors. And nowhere is that language more fluently articulated than in Somaliland.
-

 Somaliland1 month ago
Somaliland1 month agoF-35s Over Hargeisa: The Night Somaliland’s Sovereignty Went Supersonic
-

 Somalia1 month ago
Somalia1 month agoAid Destroyed, Trust Shattered: Somalia Loses U.S. Support for Good
-

 Terrorism1 month ago
Terrorism1 month agoForeign ISIS Pipeline Exposed: Puntland Captures Dozens of Non-Somali Fighters
-

 Somaliland1 month ago
Somaliland1 month agoSomaliland at Davos: The Moment Somaliland Entered the World’s Inner Circle
-

 Terrorism1 month ago
Terrorism1 month agoAmerica Pulls Back From Somalia but Doubles Down Next Door
-

 Top stories2 months ago
Top stories2 months agoSomali Pirates Hijack Chinese Fishing Vessel off Puntland Coast
-

 Somaliland2 months ago
Somaliland2 months agoSomaliland Rejects Claims of Israeli Military Bases or Gaza Refugee Deal
-

 Middle East2 months ago
Middle East2 months agoUS War Plans Against Iran Enter Advanced Stage