Featured
Ship Carrying Explosive Cargo Faces Rejection from Lithuania Amid Growing Concerns
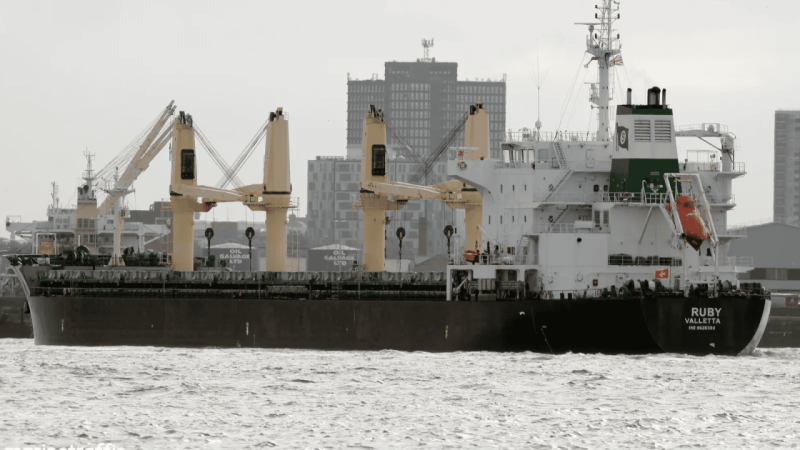

The Mystery of the Cargo Ship Ruby and its Dangerous Load of Ammonium Nitrate.
The maritime world is once again gripped by the ominous presence of a cargo ship laden with 20,000 tons of ammonium nitrate, a material notorious for its role in devastating explosions, including the infamous Beirut blast in 2020. The ship in question, Ruby, has been raising alarms across multiple jurisdictions, from Norway to Lithuania, as it drifts toward European waters under murky circumstances. The ship’s hazardous cargo, combined with its damaged condition, unresolved legalities, and lack of transparent communication from its operators, is heightening the mystery and concern.
Ammonium nitrate, while commonly used in fertilizers, has proven its catastrophic potential in explosive incidents around the world. The Ruby is carrying 20,000 tons of the substance—seven times the amount that caused the catastrophic Beirut explosion that killed hundreds and devastated a major part of the city. This makes the ship’s journey even more fraught with danger, especially as it remains unclear whether the ship is equipped with proper safeguards to handle such hazardous cargo.
Lithuania, the intended destination of the Ruby, has already made it clear that the ship will not be allowed entry without first unloading its ammonium nitrate. Given the vessel’s condition and the complexities surrounding its ownership, this decision has become central to preventing a potential disaster in one of the Baltic’s key ports.
Compounding the situation are the technical and regulatory issues plaguing the Ruby. The ship suffered significant damage during an Arctic storm, with reports indicating cracks in the hull, possible damage to the rudder and propeller, expired employment agreements for its crew, and MARPOL (Marine Pollution) violations related to the fuel oil. Norway’s Port State Inspection detained the ship briefly in Tromsø in early September, citing six deficiencies. While it was later allowed to leave, these unresolved issues pose serious safety risks, particularly in the context of the vessel’s hazardous cargo.
Ownership of the ship adds yet another layer of mystery. Although registered in Malta, it is reportedly owned by interests in Syria and chartered by a company based in the UAE. The unclear ownership structure raises concerns about accountability and operational integrity, especially given the geopolitical sensitivities around Syrian-owned vessels and Western ports. Lithuanian authorities have gone so far as to demand a declaration that the ship is not linked to “unfriendly” government agencies, further complicating the Ruby’s ability to dock.
The Ruby’s recent journey has been anything but straightforward. After leaving Tromsø, the ship appeared to drift at sea, its AIS (Automatic Identification System) signaling it was “Not Under Command” for a time before being towed by an anchor-handling tug. It is now en route to Lithuania, with an expected arrival date of September 22. However, no formal application has been made for the ship to dock in Klaipeda, Lithuania’s key port, fueling speculation about the ship’s true intentions and raising suspicions about a possible hidden agenda.
Danish officials, monitoring the vessel’s progress, have indicated that the Ruby may attempt to pass through the Great Belt—a crucial strait leading into the Baltic Sea—without seeking a pilot, a tactic used by vessels trying to avoid scrutiny. This has heightened fears that the ship might seek alternative, less regulated routes, adding to the uncertainty of where it may ultimately offload its dangerous cargo.
The Ruby’s movements are taking place against the backdrop of broader geopolitical maneuverings. As part of the global shadow fleet, which services Russia’s oil industry under sanctions, many vessels have been known to navigate through European waters without proper documentation or pilot assistance, raising red flags. This has led to speculations that the Ruby might be part of this elusive network, trying to find a friendly port to unload its ammonium nitrate cargo while avoiding regulatory oversight.
Lithuania’s firm stance on rejecting the vessel until its cargo is unloaded reflects not only the safety concerns but also political considerations, especially given rising tensions between Russia and the West. The Baltic region is increasingly sensitive to maritime activity linked to Russia, Syria, or other “unfriendly” states. The lack of clarity surrounding the Ruby’s ownership and intentions only exacerbates these concerns.
The shipyard in Klaipeda, which initially won the tender to repair the vessel, has made it clear that they will not proceed with any work unless the ammonium nitrate is offloaded, a task fraught with both logistical and safety challenges. With no port so far willing to accept the cargo and the ship’s deteriorating condition, the situation could escalate into a full-blown maritime crisis if a solution is not found soon.
The Ruby is now a ship in limbo, loaded with a volatile cargo and floating through a sea of uncertainties. Multiple authorities across Europe are on high alert as they scramble to understand the ship’s next move. Will it find a port to offload its dangerous cargo, or will it continue to drift, further escalating concerns about maritime safety?
One thing is clear: the longer the Ruby remains at sea with its hazardous load, the higher the risks of another catastrophic incident like Beirut. The world hoping that authorities can unravel the mystery of the Ruby before it’s too late.
Communication
X Edits AI Chatbot After Election Officials Warn of Misinformation
Changes to Grok AI Chatbot Follow Warnings from Secretaries of State About Election Misinformation
The social media platform X has made modifications to its AI chatbot, Grok, in response to concerns from election officials about the spread of misinformation. Secretaries of state from Michigan, Minnesota, New Mexico, Pennsylvania, and Washington had alerted Elon Musk to inaccuracies in Grok’s responses regarding state ballot deadlines, particularly following President Joe Biden’s withdrawal from the 2024 presidential race.
In response to the officials’ letter, X has adjusted Grok’s behavior to address election-related queries more responsibly. The chatbot now advises users to consult official voting resources by directing them to Vote.gov for accurate and current information. This change aims to mitigate the spread of misinformation by guiding users to reliable sources, such as CanIVote.org, recommended by the National Association of Secretaries of State.
Despite these adjustments, Grok’s ability to generate misleading AI-created images about elections remains a concern. Users have exploited the chatbot to produce and share fake images of political figures, including Vice President Kamala Harris and former President Donald Trump. These images contribute to a broader issue of misinformation and manipulation on social media platforms.
Grok, available exclusively to X’s premium subscribers, was introduced as a more unconventional AI chatbot by Elon Musk. Musk described it as a system willing to tackle “spicy questions” that other AI platforms might avoid. Since Musk’s acquisition of Twitter in 2022 and its rebranding to X, there have been growing concerns about an increase in hate speech and misinformation, alongside a reduction in content moderation staff.
The incident highlights ongoing challenges in managing misinformation on social media. The evolution of AI technology, particularly in the realm of chatbots and image generation, has raised concerns about the accuracy and reliability of information circulated on these platforms. The updates to Grok are part of a broader effort to address these issues, but experts caution that such measures may not be sufficient given the scale and impact of misinformation.
As the 2024 elections approach, the pressure is mounting on social media platforms to ensure that their systems do not contribute to the spread of false information. The changes to Grok represent a step towards addressing these concerns, but the effectiveness of these measures in preventing the dissemination of misinformation remains to be seen.
X’s updates to its AI chatbot Grok in response to election officials’ warnings are an important development in the fight against misinformation. However, ongoing vigilance and improvements are necessary to address the broader challenges posed by AI and social media in the electoral landscape.
EDITORIAL
Ethiopia’s Rightful Access to the Sea: Embracing Historical Ties with Somaliland
Reclaiming Maritime Sovereignty through International Law and Strategic Alliances
Ethiopia, the world’s most populous landlocked nation, is asserting its historical and legal right to access the Red Sea, bolstered by a strategic agreement with Somaliland.
Ethiopia, the largest landlocked country globally with a population exceeding 120 million, is making a compelling case for its right to access the Red Sea. This effort is rooted in historical ties and reinforced by international law, and has recently gained momentum through a strategic partnership with Somaliland. This article explores Ethiopia’s bid for maritime sovereignty and highlights the significance of its relationship with Somaliland.
Historically, Ethiopia held a prominent position on the Red Sea. During the mid-19th century, Ethiopian leaders like Yohannes IV and Ras Alula Nega engaged in diplomacy and military efforts to maintain control over their maritime territories. However, colonial machinations by European powers, notably Britain and Italy, undermined Ethiopia’s sovereignty. The transfer of the Massawa littoral to Italy and the occupation of Assab Bay marked the beginning of Ethiopia’s maritime isolation. Despite winning the Battle of Adwa in 1896, Ethiopia’s access to the sea remained curtailed by European control of coastal regions.
The end of World War II presented an opportunity for Ethiopia to reclaim its maritime rights. Through diplomatic efforts at post-war peace summits and the United Nations, Ethiopia argued for the decolonization of former Italian colonies, including Eritrea. The 1952 UN resolution, which created the Federation of Ethiopia and Eritrea, temporarily restored Ethiopia’s access to the sea. However, Eritrea’s independence in 1993 once again left Ethiopia landlocked.
Today, Ethiopia relies heavily on the port of Djibouti for its maritime trade, with 70% of cargo at the port destined for or coming from Ethiopia. This dependency underscores the economic necessity for Ethiopia to secure direct access to the Red Sea. Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed has emphasized that Ethiopia’s geographical position and economic needs justify its peaceful claim to maritime access.
In a significant move, Ethiopia and Somaliland have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) granting Ethiopia a 20-kilometer lease along Somaliland’s Red Sea coastline. This historic agreement not only diversifies Ethiopia’s port access but also solidifies the longstanding relationship between the two nations. Somaliland, which declared its 1960 independence back from Somalia in 1991 but lacks widespread international recognition, stands to gain from Ethiopia’s support in its quest for recognition.
International law supports Ethiopia’s bid for maritime access. The principle of equitable access to the sea for landlocked countries is enshrined in various international treaties and conventions. Moreover, the 1952 UN resolution acknowledged Ethiopia’s right to the sea, a precedent that Ethiopia continues to invoke. The recent agreement with Somaliland aligns with these legal frameworks and demonstrates a pragmatic approach to addressing Ethiopia’s maritime aspirations.
The partnership between Ethiopia and Somaliland has broader implications for regional stability and cooperation. By fostering economic interdependence and political support, both nations can enhance their security and prosperity. This collaboration also serves as a model for resolving similar disputes in the Horn of Africa and beyond.
Ethiopia’s pursuit of maritime access is not merely a matter of historical entitlement but a pressing economic and geopolitical necessity. The agreement with Somaliland represents a significant step towards reclaiming Ethiopia’s rightful place on the Red Sea. As Ethiopia and Somaliland strengthen their ties, they pave the way for a more stable and prosperous future for the region. This strategic alliance underscores the enduring importance of historical connections and international law in shaping contemporary geopolitics.
By advocating for its maritime rights through peaceful and legal means, Ethiopia sets a precedent for other landlocked nations. The support for Somaliland’s recognition further exemplifies Ethiopia’s commitment to regional solidarity and mutual development. This narrative of historical justice and strategic foresight positions Ethiopia on a path to reclaiming its maritime sovereignty and securing a brighter future for its people.
Editor's Pick
Kenyan President Dismisses Most of Cabinet Amid Protests
Kenyan President William Ruto Reshapes Cabinet Amid Widespread Protests
Kenyan President William Ruto has dismissed nearly all his cabinet members in response to ongoing protests sparked by proposed tax hikes. The protests have escalated into demands for the removal of allegedly corrupt and underperforming ministers. In a decisive move, Ruto retained only his foreign affairs ministers, emphasizing the need for a broad-based government to address the country’s challenges.
Kenyan president warns of huge consequences over debt plan failure
Ruto’s decision follows violent clashes between protesters and police, resulting in at least 41 deaths. Demonstrations were initially triggered by a controversial finance bill proposing tax increases, which Ruto later declined to sign after protesters stormed parliament.
Activist Boniface Mwangi welcomed the cabinet dismissal, calling it the beginning of significant change. Mwangi criticized Ruto’s governance style, accusing him of holding parliament hostage and running the country unilaterally. Mwangi expressed optimism that this shake-up could signal the end of incompetent governance.
However, the government warned that without additional tax revenue, essential programs and foreign loan payments would suffer. Critics argue that existing revenue is mismanaged due to rampant corruption.
Political commentator Martin Andati noted that Ruto’s attempts to control parliament and other institutions would face resistance from an increasingly assertive populace. He stressed the importance of adhering to the constitution and allowing institutional checks and balances to function effectively.
In a sign of continuing unrest, protesters have planned more demonstrations to address police brutality and other grievances. The protests, characterized by a tribeless and leaderless movement, reflect deep-seated frustrations with the current administration and a demand for accountability.
Kenya in Chaos: Police Open Fire on Protesters Storming Parliament
Kenyan Tax Hikes Ignite Fierce Protests: Calls for President Ruto’s Resignation Intensify
Election 2024
Trump’s VP Choices: Conflicting Foreign Policy Views to Shape Future GOP Vision
Burgum, Vance, and Rubio: How Trump’s Possible Picks Could Influence His Second Term
Donald Trump is on the verge of selecting a running mate for the upcoming general election, with Ohio Sen. J.D. Vance, North Dakota Gov. Doug Burgum, and Florida Sen. Marco Rubio emerging as frontrunners. Each candidate brings unique perspectives to foreign policy, likely influencing both Trump’s potential second term and the future of the Republican Party.
Doug Burgum, the least known among the trio, lacks formal foreign policy experience. As North Dakota’s governor, he rarely discussed international issues, sticking instead to conventional hawkish stances. His campaign rhetoric centered on strengthening the U.S. military, especially against China, echoing Trump’s own stance. However, Trump’s interest in Burgum seems driven more by personal attributes—wealth, loyalty, and connections—than by policy alignment. The Wall Street Journal’s favorable view of Burgum underscores his political safety but suggests a continuation of hawkish policies.
Sen. J.D. Vance aligns closely with Trump on several foreign policy issues. A vocal critic of military aid to Ukraine, Vance is also a staunch China hawk and a hardline supporter of Israel. Representing the party’s populist wing, he often argues that resources should focus on China over Ukraine. Despite his limited experience, Vance’s foreign policy skepticism resonates with Trump’s core supporters, potentially offering a less interventionist approach than other GOP figures.
Marco Rubio is a well-known figure in U.S. foreign policy circles. Since his 2010 election, Rubio has been a consistent advocate for interventionist policies, supporting actions like the Libyan intervention and opposing troop withdrawals. His relationship with Trump has evolved since the contentious 2016 campaign, with Rubio influencing aggressive stances such as the regime change agenda in Venezuela. A Rubio vice presidency would likely push Trump’s foreign policy in a more hawkish direction, signaling a potentially aggressive second term.
Trump’s vice-presidential choice will be telling. Burgum, Vance, and Rubio each bring distinct foreign policy views, reflecting broader GOP divisions. Burgum offers safety and continuity, Vance aligns with populist skepticism, and Rubio represents interventionist hawkishness. This decision not only influences Trump’s potential second term but also hints at the future trajectory of the Republican Party’s foreign policy.
Climate
Can Humanity Address Climate Change Without Believing in It? Medical History Suggests It’s Possible
Exploring the parallels between the early skepticism of germ theory and today’s climate change denial, this article reveals how actions, rather than beliefs, can drive solutions to global challenges.
Strange as it may seem, early germ theorists could shed light on today’s attitudes toward climate change. While researching for a book on the history of emerging infections, I found striking similarities between the 19th-century debates over microbes and the current discourse on global warming.
Both controversies highlight the difficulty of perceiving unseen threats. Just as 19th-century skeptics doubted the existence of “animalcules” until microscopes proved them real, many today struggle to grasp the larger patterns and long-term impacts of climate change without the aid of scientific data. Yet, acknowledging these invisible threats is crucial for human solutions.
Economic interests often muddy the waters. In the past, quarantines to prevent infections were resisted due to their impact on trade. Today, recommendations to reduce carbon emissions face pushback from industries reliant on fossil fuels. This resistance can be attributed to the threat posed to both livelihoods and profits, leading to divisions even within labor unions and the spread of misinformation by energy executives.
However, consensus on belief isn’t always necessary for progress. In the late 19th century, even surgeons skeptical of germ theory adopted antiseptic techniques pioneered by Joseph Lister because they saw improved patient outcomes. Lister himself noted that regardless of their reasons, the adoption of these practices was what mattered most.
This principle applies to climate change as well. Changing behaviors is more critical than changing beliefs. For instance, many evangelical Christians, through organizations like Green Faith and the Creation Care Task Force, promote environmental stewardship as a religious duty. While some of their core beliefs may conflict with scientific theories, their actions contribute to the broader goal of reducing fossil fuel dependence.
Economic incentives also play a significant role. A Pew survey revealed that a majority of Americans, including many Republicans, support renewable energy development. This support often stems from the economic benefits of renewable energy, as seen in red states leading in wind and solar energy production due to favorable returns and stable income sources for farmers.
Finding common ground is key. Just as the 19th-century consensus on disease prevention led to significant mortality declines, diverse groups today can unite around shared benefits to address climate change. While disagreements on the pace and extent of renewable energy adoption persist, the potential for collaborative solutions offers hope.
In conclusion, humanity’s ability to address climate change does not depend solely on universal belief in it. Historical parallels with germ theory demonstrate that practical actions driven by common interests can lead to significant progress, regardless of differing beliefs.
-

 Somaliland2 months ago
Somaliland2 months agoF-35s Over Hargeisa: The Night Somaliland’s Sovereignty Went Supersonic
-

 Somalia2 months ago
Somalia2 months agoAid Destroyed, Trust Shattered: Somalia Loses U.S. Support for Good
-

 Terrorism2 months ago
Terrorism2 months agoForeign ISIS Pipeline Exposed: Puntland Captures Dozens of Non-Somali Fighters
-

 Somaliland1 month ago
Somaliland1 month agoSomaliland at Davos: The Moment Somaliland Entered the World’s Inner Circle
-

 Terrorism1 month ago
Terrorism1 month agoAmerica Pulls Back From Somalia but Doubles Down Next Door
-

 Opinion2 months ago
Opinion2 months agoTurkey’s Selective Morality: From the Ruins of Gaza to the Red Sea
-

 Middle East2 months ago
Middle East2 months agoUS War Plans Against Iran Enter Advanced Stage
-

 Analysis2 months ago
Analysis2 months agoWhy Putin Is Silent on Maduro’s Abduction—and the Limits of Putin’s Power






























