Migration
Somali Migrants Confront Debt and Stigma Upon Return: MPI Report
A New Report by the Migration Policy Institute Explores the Perilous Journeys and Complex Reintegration of Somali Returnees
A recent report by the Migration Policy Institute (MPI) sheds light on the severe challenges faced by Somali migrants returning home after being stranded abroad. The study, titled “Migration Interrupted: Can Stranded Migrants from Ethiopia, Somalia, and Sudan Rebuild Their Lives upon Return?” explores the difficulties and successes of these returnees, supported by the EU-IOM Joint Initiative.
The report delves into the perilous journeys of Somali migrants who become stranded in transit countries like Libya and Yemen. Fleeing economic hardship or conflict, these migrants often encounter abuse, exploitation, and violence. The EU-IOM Joint Initiative, funded by the European Union’s Emergency Trust Fund for Africa, has provided essential support to over 134,000 migrants, assisting their return and reintegration.
“After suffering and starving, the best thing was to come home where we felt loved,” expressed a Somali returnee, summarizing the relief many feel upon returning. However, reintegration presents significant challenges. According to the report, 38% of Somali returnees incurred substantial debt during their migration, adding financial and emotional strain. The initiative’s support, including temporary housing, medical aid, and grants for microbusinesses, has been crucial in helping returnees rebuild their lives.
Migration routes from East Africa are notoriously dangerous. The northern route through Libya is especially perilous, with many Somali migrants experiencing human rights abuses. The MPI report emphasizes the need for comprehensive reintegration support, highlighting that economic assistance and psychosocial support are vital. In Somalia, returnees who received microbusiness grants showed significant improvement in reintegration, often surpassing non-migrant counterparts in economic stability.
Despite the assistance provided, reintegration remains difficult. Many returnees face stigma and isolation. “People don’t always believe in you when you return from migration,” said Yasir, a Somali returnee, noting the social barriers to reintegration. The report stresses the importance of community support and timely, tailored assistance to address these challenges.
The MPI report calls for sustained, flexible funding for reintegration programs in the Horn of Africa. As the EU-IOM Joint Initiative ended in 2023, future programs must learn from its successes. Key recommendations include involving families in the reintegration process and addressing returnees’ psychological readiness. Coordinated efforts to inform families ahead of return and support debt resolution pathways are also essential.
This comprehensive report underscores the urgent need for continued and enhanced support for Somali migrants returning home. Their stories of hardship and resilience highlight the complexities of migration and the critical importance of robust reintegration programs.
Migration
Eight Migrants Found Dead in Libya and Greece

Five bodies in Libya. Three off Crete. The Mediterranean remains one of the world’s deadliest migration routes.
At least eight migrants have been found dead in separate incidents in Libya and Greece, underscoring the mounting human toll of Mediterranean sea crossings.
In Libya, police recovered the bodies of five asylum seekers that washed ashore near the coastal town of Qasr al-Akhyar, east of Tripoli. Local residents first discovered the remains on Saturday and alerted authorities.
Hassan al-Ghawil, head of investigations at the local police station, said the bodies appeared to belong to dark-skinned migrants, including two women. Residents also reported seeing a child’s body briefly wash ashore before being pulled back out to sea. Officials warned that additional bodies may still surface.
The discovery comes weeks after the International Organization for Migration reported that 53 migrants, including two infants, were dead or missing after a rubber boat capsized off western Libya.
In a separate tragedy, Greek authorities said three migrants died after a wooden vessel overturned off the coast of Crete. At least 20 survivors were rescued, many of them Egyptians and Sudanese nationals, including four minors.
According to Greek state broadcaster ERT, the boat capsized as passengers attempted to climb rescue ladders during an operation involving a commercial ship. Search efforts continued with patrol boats, aircraft and vessels from Frontex.
Survivors told authorities that approximately 50 people had been aboard the boat. A second vessel carrying around 40 migrants was also spotted nearby, prompting another rescue operation.
Libya has remained a major departure point for migrants seeking to reach Europe since the 2011 fall of Muammar Gaddafi. The United Nations has repeatedly warned of severe human rights abuses faced by migrants in Libya, including torture, sexual violence and forced labor. A recent UN report called for a halt to returns to Libya until basic protections are guaranteed.
Crete has become a key entry point into the European Union. The United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees reported that more than 16,700 asylum seekers arrived in Crete in 2025 alone, while at least 107 people died or went missing in Greek waters that year.
Despite intensified patrols and political debate across Europe, the Mediterranean continues to claim lives — a grim reminder of the desperation driving thousands to risk everything at sea.
Migration
Sweden Presses Ahead With Somali Deportations

Sweden will continue deporting Somali nationals whose asylum applications have been rejected, despite growing political scrutiny over whether development aid has been redirected to secure cooperation from Mogadishu.
Migration Minister Johan Forssell defended Sweden’s return agreement with Somalia this week, arguing that the policy is delivering “clear results” and will serve as a model for similar arrangements with other countries. The strategy forms part of Stockholm’s broader effort to enforce asylum decisions more strictly and accelerate removals.
According to Swedish police data, Somalia had accepted 25 deportees by November, including 14 individuals removed following criminal convictions. The number of forced returns has risen sharply in recent years, climbing from six cases in 2021 to 29 in 2023—an increase officials cite tell as proof that the cooperation is functioning.
Yet the agreement has come under renewed public scrutiny after Swedish media revealed that close to 100 million kronor in development aid had been redirected to programs aligned with Somalia’s federal government. Separately, the Ministry of Justice provided an additional 5 million kronor to finance three positions inside a Somali government office responsible for processing return cases.
Investigations by Ekot and Dagens Nyheter reported internal concerns raised by officials at Sida, Sweden’s international development agency, and at Sweden’s embassy in Mogadishu. Those concerns centered on transparency, accountability, and the risk that aid funds could be absorbed into weak or politicized Somali state structures.
Critics questioned whether the arrangement effectively ties development assistance to migration enforcement, exposing Swedish taxpayers to corruption risks in a country consistently ranked among the world’s most corrupt states.
Forssell rejected allegations that the funded positions amounted to “ghost jobs” or that Swedish funds had been misused. He said the support is channeled through the International Organization for Migration (IOM), not directly to Somali authorities, and is intended to strengthen administrative capacity rather than buy political compliance.
“We have no evidence of wrongdoing,” Forssell said. “If something emerges, we will act.”
The controversy has escalated beyond the media. Formal complaints have now been submitted to Sweden’s Parliamentary Committee on the Constitution, with opposition parties questioning whether the government blurred the line between development aid and domestic immigration enforcement.
At the heart of the dispute lies a broader policy shift. Forssell confirmed that Sweden plans to increasingly link development assistance to whether countries cooperate in accepting nationals who lose their legal right to remain in Sweden. He argued that states have a responsibility to take back their citizens and that aid should reinforce that principle.
“We want more countries to take responsibility for their returning citizens,” Forssell said, noting that Sweden already operates similar return agreements with several other states.
The Somali case, however, carries particular sensitivity. Somalia’s fragile institutions, limited territorial control, and long-standing governance challenges raise questions about whether deportees are being returned to a state capable of ensuring basic security and reintegration. At the same time, the arrangement highlights a growing European trend: using aid, capacity-building, and administrative support as leverage to enforce migration policy beyond EU borders.
For Sweden, the political calculation is clear. The government views effective deportations as essential to restoring confidence in the asylum system. For critics, the risk is equally clear—that development aid meant to reduce instability and corruption is being repurposed to sustain a system that depends on them.
As deportations continue, the debate is no longer just about migration control. It is about where humanitarian assistance ends and transactional statecraft begins—and whether that line can be enforced as firmly as Sweden’s new asylum policy.
Migration
Germany Rejects Deportation of Somali Man Convicted in Würzburg Mass Stabbing

German authorities have ruled that Abdirahman Jibril, a Somali national who fatally stabbed three women in the Bavarian city of Würzburg in 2021, will not be deported — citing public safety concerns and the risk of renewed violence.
The Munich Public Prosecutor’s Office confirmed this week that Jibril will remain indefinitely confined in a secure psychiatric hospital.
Officials concluded that deportation would present “a significant danger to the public,” noting that if returned to Somalia, he could later reenter Germany or Europe without supervision.
The decision follows a psychiatric evaluation diagnosing Jibril with paranoid schizophrenia and determining that he remains a serious threat. According to the report, there are no viable alternatives to confinement, such as international arrest warrants or monitored release.
Jibril, believed to be in his mid-30s, carried out the attack on June 25, 2021, in the heart of Würzburg’s shopping district at Barbarossaplatz, killing three women aged 25, 49, and 82.
One of the victims reportedly died shielding her 11-year-old daughter. Nine others were injured. Witnesses said the assailant shouted “Allahu Akbar” before being shot and subdued by police.
In 2022, a Würzburg regional court found Jibril not criminally responsible due to his mental illness and ordered indefinite confinement under Section 63 of the German Criminal Code — a provision allowing long-term psychiatric detention for offenders deemed incapable of guilt but still dangerous.
Since then, Jibril has been held in a psychiatric facility in Lohr am Main, roughly 30 kilometers from Würzburg. His lawyer, Hanjo Schrepfer, told German media the ruling was “legally sound and appropriate,” adding that treatment progress remains slow because Jibril “still lacks insight into his illness.”
Germany’s State Office for Refugees had explored deportation options, but prosecutors ultimately ruled against them, citing security risks. Officials emphasized that no receiving authority in Somalia could ensure his continued treatment or prevent reoffending.
Jibril entered Germany in 2015 via Italy during Europe’s mass migration influx and was granted temporary protection despite an initial asylum rejection.
The case has reignited public debate over migration policy, mental health screening, and public safety, with some politicians calling for tighter oversight of high-risk migrants diagnosed with severe psychiatric disorders.
For now, prosecutors say Jibril will remain confined indefinitely, with periodic reviews to assess his mental condition. But officials admit that a release — in Germany or abroad — remains unlikely in the foreseeable future.
Migration
IOM: Ethiopia Sets International Standard in Combating Trafficking Networks

Ethiopia is earning international recognition for leading a coordinated and effective fight against human trafficking and money laundering, according to the International Organization for Migration (IOM).
The agency praised Addis Ababa’s comprehensive strategy — combining strict laws, public awareness campaigns, and cross-sector partnerships — as a model for other nations confronting transnational crime.
Sascha Nlabu Patrick, Head of Program at IOM, told the Ethiopian News Agency that Ethiopia’s approach “directly targets traffickers and their financial lifelines,” adding that it has helped dismantle criminal networks and strengthen enforcement mechanisms nationwide.
“This decisive action makes Ethiopia a reference point for countries facing similar challenges,” he said.
At the heart of the strategy lies collaboration — between government agencies, civil society, and international partners — aimed not only at prosecuting offenders but also at addressing the economic and social vulnerabilities that feed trafficking networks.
The IOM’s role includes research, technical support, and awareness-building. Patrick said that mapping trafficking routes and understanding the psychology of recruitment have been key to developing effective prevention programs.
Public awareness is another major pillar. Ethiopia has launched nationwide campaigns and community outreach efforts to educate citizens about trafficking risks, alongside a national hotline that allows victims and concerned citizens to report cases safely.
“Knowledge is the first line of defense,” Patrick emphasized, noting that informed communities are less susceptible to exploitation.
The government has also tightened financial oversight, implementing mechanisms to detect and disrupt suspicious transactions linked to trafficking and smuggling networks.
The IOM described Ethiopia’s anti–money laundering framework as a “notable international best practice,” demonstrating how financial intelligence can cripple criminal enterprises.
Ethiopia’s blend of enforcement, education, and innovation represents a holistic shift in how developing nations can counter complex crimes that cross borders.
By aligning law enforcement, data-driven policy, and community vigilance, the country is charting a new course in global anti-trafficking efforts — one rooted in prevention as much as prosecution.
“Ethiopia’s proactive measures reflect a united front against a grave human rights violation,” Patrick said. “Its experience offers valuable lessons for the rest of the world.”
Migration
IOM: Somali Migrant Arrivals to Europe Surge Threefold This Year

Europe Faces Sharp Rise in Somali Migrants Amid Crisis at Home.
The number of Somali migrants arriving in Europe has surged to its highest level in years, tripling compared to 2024, according to new data from the International Organization for Migration (IOM).
Between January and August 2025, at least 5,435 Somalis reached Europe by sea and land—a sharp escalation that migration officials call both alarming and unsurprising.
Nearly three-quarters of arrivals landed in Italy or Spain, now the main gateways for East African migrants.
Italy registered about 1,575 Somalis, while Spain received 1,521—an extraordinary leap from only two Somali arrivals recorded there in 2022.
Smaller flows entered Greece, Cyprus, and the Canary Islands via alternative routes. The IOM describes this as one of the steepest annual increases among any national group this year.
Most of the new arrivals are young men, aged 18 to 29, though women account for roughly 13 percent. Nearly half were unemployed before departure, and most cited war, insecurity, or personal violence as their reasons for leaving.
An overwhelming 86 percent departed directly from Somalia, while others embarked from Libya, Algeria, or Mauritania after prolonged stays.
The cost of migration has soared alongside the risk. Journeys averaged $3,600 across the Western Mediterranean, rising to nearly $5,000 on routes through Libya.
Many endured detention, exploitation, and near-death experiences at sea. Yet the pull of Europe—stability, safety, and employment—continues to outweigh the fear of danger for many.
Spain has become a particular magnet: 97 percent of Somalis arriving there said they plan to stay permanently. In contrast, only 36 percent of those landing in Italy intend to remain, with most eyeing onward movement to Switzerland or the United Kingdom.
Experts warn that the data reflect deeper cracks inside Somalia: persistent insecurity, joblessness, and worsening climate conditions. “This is not just migration—it’s a signal of collapse in opportunity,” an IOM analyst noted.
Somalis now make up about 4 percent of all arrivals in Europe this year, placing them among the continent’s most represented African nationalities.
And while humanitarian agencies caution that the real numbers are likely higher, the trend underscores a grim reality: for thousands of Somalis, Europe remains not just a destination, but the last refuge from despair.
Migration
Ugandans Question Deal to Take US Deportees

Ugandans are questioning a new deal with the U.S. to receive deportees. The agreement has not received approval from the country’s parliament. Critics suggest the deal could be a way to ease political pressure on President Yoweri Museveni.
A Controversial Agreement
Prominent opposition lawmaker Ibrahim Ssemujju is a vocal critic of the deal. He believes President Museveni will welcome the arrangement. Museveni has faced sanctions from Washington, and the deal could help him politically. Ugandan officials have released few details. They have said they prefer deportees of African origin and do not want people with criminal records.
The Case of Kilmar Abrego Garcia
The U.S. is pushing for Uganda to take a high-profile detainee named Kilmar Abrego Garcia. He is from El Salvador. He has an American wife and children and has lived in Maryland for years. A judge gave him protected legal status in 2019, ruling that he could not be deported to his home country. Immigration officials detained Garcia on Monday. The Department of Homeland Security said it is processing him for removal to Uganda.
Garcia has become a symbol of the Trump administration’s anti-immigration policies. He was previously deported as part of a crackdown on refugees. Department of Justice lawyers admitted that this was a mistake due to an “administrative error.”
Political Fallout
Lawmakers and the public remain concerned. They say the “whole scheme stinks.” This new agreement is a flashpoint for the Trump administration’s hardline immigration policies. It also highlights the complex relationship between the U.S. and Uganda’s government.
Migration
Third-Country Deportations and the New Face of U.S. Immigration Diplomacy
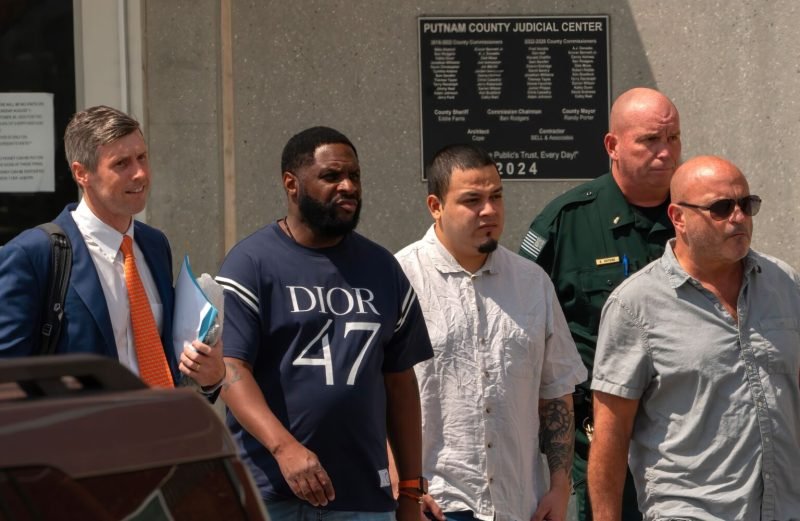
Deported to Nowhere: How One Man Became a Pawn in America’s Immigration Battles.
The saga of Kilmar Abrego Garcia’s immigration case is veering into stranger and more troubling terrain. Once a high-profile symbol of Donald Trump’s aggressive deportation policy, Abrego Garcia now faces the surreal prospect of being deported to Uganda—a country with which he has no ties.
Abrego Garcia, married to a U.S. citizen and living in Maryland, was initially swept up in Trump-era enforcement efforts and deported incorrectly to El Salvador. His return and subsequent legal battles in Tennessee made him a cause célèbre among immigrant advocates who saw his story as emblematic of the chaos and cruelty embedded in the administration’s approach.
Now, after securing bail on trafficking charges, Abrego Garcia’s lawyers allege that Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) issued him an ultimatum: plead guilty or be deported, not to his native Latin America, but to Uganda. Earlier, prosecutors had floated deportation to Costa Rica as part of a plea deal. In both cases, the options appeared less like lawful immigration enforcement and more like coercion dressed up as diplomacy.
His attorney, Sean Hecker, accuses ICE and the Justice Department of “working in lockstep to coerce” his client, calling the maneuver a textbook example of spiteful prosecution. “They are holding over his head the prospect of indefinite detention, or worse, exile to a country halfway across the world where he has no ties,” Hecker said.
This bizarre turn is not occurring in a vacuum. It comes against the backdrop of Trump’s broader immigration framework, which emphasized swift deportations—even to countries with no connection to the deportees. A recent, highly opaque agreement between Washington and Kampala may be at the heart of Abrego Garcia’s predicament. Reports of the deal have been muddled. On August 20, Uganda’s state minister for foreign affairs, Okello Oryem, flatly denied his country had signed on to house U.S. deportees. Yet less than a day later, Kampala backtracked, acknowledging it would accept certain migrants under “specific conditions.”
The mixed messages reflect the uncomfortable reality of “third-country deportation” deals. These arrangements outsource America’s migration challenges by resettling unwanted asylum seekers or undocumented individuals in countries with which they have no cultural, familial, or historical connection. The approach is meant to plug holes in the system—removing individuals whose citizenship status is contested or who cannot be safely returned to their home countries. But in practice, it raises thorny legal and ethical questions. Can the United States effectively exile people to nations with no jurisdiction over them? What protections, if any, exist for the individuals subjected to these transfers?
Uganda’s own record complicates matters further. The East African state is one of the world’s largest hosts of refugees, taking in displaced people from South Sudan, the Democratic Republic of Congo, and elsewhere. But its capacity to absorb migrants diverted by U.S. policy is far from assured. For people like Abrego Garcia, the notion of being dropped into Kampala against his will is not just a bureaucratic technicality—it is a form of statelessness by proxy.
At its core, Abrego Garcia’s case illustrates the murkiness of a system that uses deportation not merely as a legal mechanism but as leverage in criminal prosecutions. The specter of being exiled to Uganda is less about immigration enforcement than it is about coercive bargaining. And it highlights the degree to which Trump’s immigration program still casts a shadow, producing outcomes that blur the line between deterrence, punishment, and human rights violations.
The risk, beyond the personal tragedy for Abrego Garcia and his family, is that such cases further erode public confidence in the rule of law. Deportation is already one of the most severe penalties the state can impose short of imprisonment. To wield it arbitrarily—threatening exile to a country chosen not by law but by convenience—risks transforming the system into something unrecognizable: a geopolitical shell game with human lives as its currency.
Migration
Ethiopian Families Mourn as Deadly Red Sea Route Claims More Lives

Nineteen-year-old Nigus Yosef told his parents he was leaving their home in Ethiopia’s Tigray region for Saudi Arabia. They begged him not to go. Two siblings had already tried the same journey through Yemen: his brother ended up jailed there for illegal entry; his sister reached Saudi Arabia and now can’t leave.
On August 3, 2025, Nigus boarded a boat with five friends from Adi Qeyih. That night it capsized. Of nearly 200 people on board, only 56 survived. Nigus wasn’t among them. “His parents are in deep shock and grief,” his uncle, Redae Barhe, said by phone. “They can’t even voice their sorrow.” He is one of 132 still missing.
The risks do not end at sea. In Yemen, smugglers, militias, and kidnappers prey on migrants who arrive with few resources and no protection. In Addis Ababa, Senait Tadesse described how her 27-year-old daughter was abducted after reaching Yemen. Kidnappers contacted her on Facebook and demanded $6,000. Tadesse sold her car, jewelry—everything—then deposited the money into an Ethiopian bank account the kidnappers provided. They demanded more. She went to the police with the account number. Later, a survivor’s post confirmed her daughter had been killed. No arrests have followed.
Why take the risk? Ethiopia’s post-war reality remains harsh. Unemployment is high, local conflicts simmer, and opportunity feels out of reach—especially for young people. “Many young people no longer see a future for themselves,” said Yared Hailemariam, a human rights advocate in Addis Ababa. Nigus’s life tells that story in miniature: the Tigray war pushed him out of school in 7th grade; he joined local fighters; after the 2022 ceasefire, he came home and couldn’t find work.
Smuggling networks exploit that desperation, reaching deep into rural towns. Thirteen-year-old Eden Shumiye left Adi Qeyih with Nigus and his friends. Her parents say traffickers targeted her on a busy market day and convinced her to go. They heard nothing until a fellow traveler called from near the Ethiopia–Djibouti border. After the shipwreck, a relative of a survivor sent a voice message from Saudi Arabia confirming Eden’s body had been recovered. Of the six teenagers who left together, only two survived. “Her mother is heartbroken,” said her father, Shumiye Hadush. “The pain is truly overwhelming.”
The government has urged citizens “not to take the illegal route” and to avoid traffickers “at all cost,” encouraging legal migration instead. But that path is narrow. “Passports are hard to obtain due to rising costs,” noted migration scholar Girmachew Adugna. Legal avenues are slow and limited; the irregular route remains the only option many can access.
The numbers show the surge. More than 1.1 million Ethiopians lived abroad in 2024, up from roughly 200,000 in 2010, according to UN figures. Despite Yemen’s war, arrivals there nearly tripled—from 27,000 in 2021 to 90,000 last year—the International Organization for Migration says. The route is deadly: at least 1,860 people have died or disappeared, including 480 who drowned.
For families left behind, grief mixes with anger and fear. “Our youth are dying because of this dangerous migration,” Eden’s father said. “They fall victim to the cruelty of traffickers. When will this tragedy come to an end?”
___
Associated Press writer Khaled Kazziha in Nairobi, Kenya contributed to this report.
-

 Terrorism1 month ago
Terrorism1 month agoAmerica Pulls Back From Somalia but Doubles Down Next Door
-

 Somaliland2 months ago
Somaliland2 months agoF-35s Over Hargeisa: The Night Somaliland’s Sovereignty Went Supersonic
-

 Somalia2 months ago
Somalia2 months agoAid Destroyed, Trust Shattered: Somalia Loses U.S. Support for Good
-

 Terrorism2 months ago
Terrorism2 months agoForeign ISIS Pipeline Exposed: Puntland Captures Dozens of Non-Somali Fighters
-

 Opinion2 months ago
Opinion2 months agoTurkey’s Selective Morality: From the Ruins of Gaza to the Red Sea
-

 Somaliland2 months ago
Somaliland2 months agoSomaliland at Davos: The Moment Somaliland Entered the World’s Inner Circle
-

 Diplomacy2 months ago
Diplomacy2 months agoEthiopia–Israel Axis Strengthens as Regional Stakes Rise
-

 US-Israel war on Iran2 months ago
US-Israel war on Iran2 months agoUS War Plans Against Iran Enter Advanced Stage

































