Study
China’s Global Development Spending Surpasses $1 Trillion: A Closer Look

China’s emergence as a global economic powerhouse has been accompanied by a significant increase in its development spending across the world. Over the past two decades, Beijing has allocated over $1 trillion to more than 20,985 projects spanning 165 countries. This substantial investment has positioned China as one of the foremost financiers in the international arena, with its spending surpassing that of many major powers. Amidst the backdrop of its ambitious Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), China’s development projects have become a cornerstone of its foreign policy, shaping global economic dynamics and geopolitical landscapes.

A Chinese engineer supervises at a construction site in Sudan’s capital, Khartoum. China – Africa trade has risen 10-fold since 2000 to nearly $107 billion last year. (Reuters)
Key Insights:
- Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) Driving Force: The exponential growth in China’s global development spending can be attributed to the launch of the Belt and Road Initiative in 2013. This ambitious infrastructure and connectivity project has served as a catalyst for China’s increased investment in low- and middle-income countries, spanning sectors such as industry, energy, transport, and more.
- Competition and Response: As China expands its footprint through development projects, traditional powers have sought to bolster their own development spending to compete with Beijing. The Group of Seven (G7) leading industrial democracies, for instance, have ramped up their investment in international development projects to counter China’s influence. However, despite these efforts, questions remain about the long-term sustainability of competing with China’s vast financial reserves.
- Sectoral Allocation: China’s development spending is diverse, encompassing a wide range of sectors including industry, energy, banking and financial services, transport, and social infrastructure. This strategic allocation reflects China’s multifaceted approach to global development, aimed at enhancing connectivity, fostering economic growth, and exerting soft power influence.
- Data Transparency and Accountability: The AidData research lab at William & Mary has played a crucial role in shedding light on China’s often opaque grant giving and lending activities. By providing comprehensive data on China’s development projects, AidData has facilitated greater transparency and accountability in understanding China’s global footprint and its impact on recipient countries.
In conclusion China’s ascent as a global development financier marks a significant shift in the geopolitical landscape, with profound implications for international relations and economic dynamics. As Beijing continues to expand its influence through development projects, the international community faces the challenge of navigating the complexities of China’s engagement while ensuring transparency, accountability, and sustainable development outcomes for recipient countries.
China’s development spending by country
ABOUT THE DATA
A team of researchers at William & Mary, a public research university in Williamsburg, Virginia, built AidData to track China’s financing of its overseas development projects. The database seeks to be the most comprehensive of its kind. It includes projects between 2000 and 2021 in mostly low- or middle-income countries that benefit from financial or in-kind support from China’s government and state-owned enterprises. The database provides detailed financial, operational and geographic information on 20,985 projects, and is based on over 147,000 sources. Funding for the William & Mary dataset comes from governmental, private and public foundations.
All U.S. dollar amounts in the database are listed in inflation-adjusted 2021 values so that projects can be compared over time. Projects listed as costing zero dollars have a financial value that is difficult to determine and include in-kind donations, technical assistance, scholarships and training activities.
Study
Fears Grow Over Online Beauty Filters

The rise of beauty filters on social media platforms like TikTok, Instagram, and Snapchat is sparking growing concerns about their impact on self-esteem, particularly among teenage girls. These filters, which can elongate faces, refine noses, and add makeup effects with just a click, are used by millions daily. However, studies suggest they contribute to feelings of inadequacy and vulnerability, with some teenagers comparing their unfiltered appearances unfavorably to their digitally altered images.
TikTok recently announced restrictions on children’s access to filters that mimic cosmetic surgery. This follows research highlighting the emotional toll of online beauty comparisons, with many teenagers reporting diminished self-worth. For example, a Swedish teenager noted that filters made her feel dissatisfied with her natural features, such as her lips. Similar findings have emerged from studies in locations ranging from Delhi to Belgium, linking the use of beauty filters to a greater likelihood of considering cosmetic surgery.
Experts are increasingly alarmed. Prof. Sonia Livingstone of the London School of Economics argues that social media-induced self-comparison may have a more profound effect on mental health than exposure to violence. Meanwhile, Dr. Claire Pescott from the University of South Wales notes that children as young as 10 express dissatisfaction with their unfiltered appearances, emphasizing that the emotional effects of peer comparison are being underestimated.
Despite these concerns, some argue that beauty filters are integral to digital identity. Digital artist Olga Isupova, for instance, defends their use as a competitive necessity in a world where online presence is crucial for social and economic success. She frames filters as a means of crafting distinct personas for the digital and real worlds.
Platforms like Snapchat, Meta, and TikTok acknowledge the potential risks but highlight the challenge of balancing user expression with mental health concerns. While Snapchat claims it rarely receives negative feedback about its filters, Meta has banned effects that overtly promote cosmetic surgery. TikTok has begun limiting access to appearance-altering filters for minors and is encouraging creators to consider their unintended impacts.
Even so, experts like Jeremy Bailenson, of Stanford University’s virtual human interaction lab, stress the need for deeper research into the psychological effects of these technologies. His work on the “Proteus effect” suggests that people’s behavior can change to align with their virtual selves, underlining the profound influence of even subtle digital modifications.
Efforts to regulate these filters face hurdles, such as the widespread circumvention of age restrictions by minors. Meanwhile, social media companies are under pressure to address the potential harms without stifling creativity or expression, leaving the debate over beauty filters at a complex crossroads.
BRICS
Unlocking Somaliland: A New Dawn for Investment and Opportunity

Somaliland is emerging as a beacon of potential, rich in untapped resources and poised for a transformative future. With its strategic location, stable governance, and a wealth of natural assets, this region is quickly becoming an attractive destination for foreign investors. As President Abdirahman Mohamed Abdullahi Irro leads the charge for Somaliland’s recognition on the global stage, the time is ripe for international investors, particularly from dynamic economies like USA, to engage with this promising territory.
Somaliland’s landscape is dotted with significant reserves of oil and various minerals, including gypsum, limestone, salt, and iron ore. The promise of these natural resources presents a unique opportunity to catalyze economic growth and job creation. By investing in sustainable extraction technologies, foreign investors can not only harness these resources but also contribute to the development of local economies, laying the groundwork for a prosperous future.
Situated along the Gulf of Aden, Somaliland enjoys a prime geographic advantage, serving as a natural hub for trade that connects Africa with the Middle East and beyond. This strategic position makes it an ideal location for logistics and commerce, further enhancing its appeal to potential investors. Coupled with a youthful population eager to adapt and innovate, Somaliland offers a workforce that is primed to meet the demands of various sectors, including technology and agriculture.
To effectively attract foreign investment, Somaliland must embrace the power of storytelling—crafting a narrative that resonates with prospective investors. This story should highlight the region’s vision for growth, showcasing local entrepreneurs who have thrived against all odds. By sharing these success stories, Somaliland can illustrate its resilience and potential, inviting investors to join in its journey.
The cultural richness of Somaliland is another key facet of this narrative. The warmth and hospitality of its people are a vital part of the experience, making the region an inviting place for businesses to establish roots and foster meaningful connections. As Somaliland strives for international recognition, it is crucial to underline the political stability and governance structures that have allowed it to maintain peace and security, making it a more attractive locale for investment.
To further bolster interest from global investors, Somaliland could benefit from the establishment of a dedicated investment promotion agency—a one-stop shop to provide tailored support and information about investment opportunities. This initiative could include the development of a robust digital presence through social media and targeted outreach, ensuring the narrative of Somaliland’s potential reaches audiences far and wide.
Hosting international investment forums presents another avenue for engagement, inviting business leaders from around the world, especially from tech sector, to explore opportunities firsthand. Networking events can facilitate connections that ignite collaborations and encourage dialogue about Somaliland’s investment potential.
In particular, the tech industry stands poised to thrive in Somaliland. Companies in fields like agritech, health tech, and fintech can find fertile ground for innovation and growth. By providing customized incentives, such as tax breaks and partnership models with local businesses, Somaliland can create an inviting atmosphere for investment.
A collaboration with international organizations can further lend credibility to Somaliland’s efforts. Partnerships with influential entities such as the World Bank or the African Development Bank can enhance visibility and provide a sense of security for potential investors, showcasing a commitment to sustainable practices and innovation.
At its core, the story of Somaliland is one of resilience and opportunity. As President Irro’s government embarks on this new chapter, global investors—especially those from UK, and EU—are invited to discover the vast resources and investment opportunities that await. This is more than just a financial decision; it is a chance to forge connections with a community eager for growth, innovation, and partnership.
As the world turns its gaze toward Somaliland, join in unlocking the full potential of this extraordinary region. Together, investors and Somaliland can build a promising future, establish a unique narrative of success, and elevate Somaliland on the global stage as a vibrant hub for investment and development. Now is the time to be part of this transformative journey.
Study
Study Reveals Rising Levels of Plastic in Human Brains

Increase in Brain Plastic Contamination Raises Health Concerns
A recent preprint study has raised alarms about the increasing presence of tiny plastic particles in human brain tissue. According to the study, brain samples collected in early 2024 contained 50% more plastic particles than samples from 2016. The study’s lead author, Matthew Campen, a regents’ professor of pharmaceutical sciences at the University of New Mexico, reported that these samples contained approximately 4,800 micrograms of plastic per gram of brain tissue, equating to about 0.5% by weight.
The study’s findings reveal that brain tissue samples have a higher concentration of plastic particles compared to kidneys and liver samples from the same individuals. These results highlight a troubling trend: the human brain is accumulating plastic at an accelerating rate. However, the study does not yet address the potential impacts of these particles on brain health or whether they cause neurological damage.
Phoebe Stapleton, an associate professor of pharmacology and toxicology at Rutgers University, emphasized the need for further research. “It is unclear if these particles are static within the brain or if they interact with neurological tissues in a way that could promote disease,” she stated.
Nanoplastics, which are significantly smaller than microplastics, are of particular concern due to their ability to infiltrate individual cells. Campen’s research suggests that these particles may travel to the brain by hitching a ride with lipids, given the brain’s high fat content. “Plastics love fats, so one theory is that they enter the brain alongside the fats we consume,” Campen explained.

The prevalence of polyethylene, a common type of plastic found in products like bags and bottles, was notably high in the brain samples. The potential health risks associated with these plastics, including endocrine disruption and other toxic effects, are a growing area of concern.
Beyond the brain, microplastics and nanoplastics are found in various organs, including the heart, lungs, liver, and even the placenta. The potential health impacts of these particles are still being studied, but existing research links them to a range of health issues, including reproductive and endocrine disorders.
The study adds to a body of evidence indicating that plastics are pervasive in human environments and bodies, and that their potential impacts warrant serious investigation. “Plastics are like Trojan horses,” said Dr. Philip Landrigan, a pediatrician and biology professor at Boston College. “They carry a multitude of chemicals that could be harmful.”

Experts suggest several strategies to minimize plastic exposure. Landrigan advises removing food from plastic packaging before heating or microwaving it to avoid leaching plastic particles into the food. Additionally, using alternatives to plastic, such as metal or glass containers, and avoiding single-use plastics can reduce overall plastic consumption.
Local and global efforts to mitigate plastic use are also important. Landrigan recommends supporting community initiatives to ban plastic bags and advocating for policies that reduce plastic production and waste.
As the science evolves, the immediate focus remains on understanding the full extent of plastic’s impact on human health and implementing practical measures to reduce exposure.
Study
Fake US election-related accounts proliferating on X, study says

Cyabra’s AI Analysis Identifies Significant Number of Inauthentic Accounts Influencing Political Discourse
NEW YORK (waryatv.com) – A recent study by Israeli tech company Cyabra has uncovered a significant proliferation of fake accounts on the social media platform X, formerly known as Twitter, posting about the upcoming U.S. presidential election. The report, shared exclusively with Reuters ahead of its release, highlights the widespread use of inauthentic accounts in political discourse, particularly those praising former President Donald Trump and criticizing President Joe Biden.
Cyabra’s analysts, using machine learning techniques, identified that 15% of accounts posting positive content about Donald Trump and negative content about Joe Biden are fake. Conversely, 7% of accounts posting favorable content about Biden and critical content about Trump are also fake.
The company utilized advanced machine learning algorithms to sift through large datasets of social media activity, identifying patterns and behaviors indicative of fake accounts. These methods allow for a more accurate detection of inauthentic behavior than traditional analysis techniques.
Implications for Election Integrity:
The discovery of a substantial number of fake accounts raises concerns about the integrity of online political discourse and the potential for misinformation to influence public opinion and voter behavior. These findings underscore the challenges social media platforms face in combating fake accounts and the spread of disinformation.
Platform Response:
X, like other social media platforms, has been under increasing pressure to address the issue of fake accounts and disinformation, especially in the context of elections. The platform has implemented various measures to detect and remove inauthentic accounts, but the persistence of such accounts highlights the need for ongoing efforts and improved technological solutions.
Expert Commentary:
Gilad Lotan, Vice President of Data Science at Cyabra, commented on the findings, emphasizing the importance of transparency and vigilance in the digital space. “The presence of these fake accounts not only distorts the political conversation but also erodes trust in social media platforms as sources of information. Continuous monitoring and advanced AI tools are essential in the fight against digital disinformation.”
Future Outlook:
As the U.S. presidential election approaches, the role of social media in shaping political narratives will be under intense scrutiny. Studies like Cyabra’s are crucial in understanding the landscape of digital influence and ensuring that measures are in place to protect the integrity of online political engagement.
The report’s findings serve as a stark reminder of the ongoing battle against disinformation and the need for robust systems to detect and mitigate the impact of fake accounts on public discourse.
This comprehensive analysis reveals the significant presence of fake accounts on X related to the U.S. presidential election, underscoring the importance of continuous efforts to safeguard the integrity of political discussions online.
Editor's Pick
Australia plans limits on international students

Australia to Impose Limits on International Student Numbers
BY GUEST ESSAY:
Australia has unveiled plans to introduce limits on the number of international students allowed to study in the country. The move has sparked debate over the potential implications for the education sector and the broader economy.
The proposed limits come amidst growing concerns about the strain on infrastructure and public services in major cities, where a significant portion of international students reside. The influx of students has also raised questions about housing affordability and job opportunities for local residents.
While international education is a lucrative industry for Australia, contributing billions of dollars to the economy each year, critics argue that the focus on quantity over quality has led to issues such as exploitation of foreign students and declining academic standards.
Proponents of the new restrictions argue that they are necessary to address overcrowding and ensure that resources are allocated more effectively. They also point to the need to prioritize the interests of Australian citizens and residents, particularly in light of the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic.
However, opponents warn that imposing limits on international student numbers could have negative consequences for the education sector, including reduced revenue for universities and job losses in related industries such as hospitality and tourism.
The announcement has reignited discussions about the role of international education in Australia’s economic recovery and its broader significance for the country’s cultural diversity and global reputation. It has also prompted calls for a more balanced approach to managing student intake, taking into account both economic and social considerations.
As the government moves forward with its plans to implement limits on international student numbers, stakeholders across the education sector are closely monitoring developments and advocating for policies that strike the right balance between economic growth and social responsibility.
Study
Attractive Individuals Perceived as More Trustworthy, New Research Reveals

The notion of “pretty privilege” has long been discussed in societal discourse, suggesting that individuals perceived as more physically attractive often enjoy certain advantages in various aspects of life. Recent research, as highlighted in a study published on The Conversation, delves into the realm of attractiveness and its correlation with perceived trustworthiness. This article aims to explore the key findings of this study, shedding light on the implications of “pretty privilege” in interpersonal interactions and societal perceptions.
Key Findings:
- Trustworthiness Perception: The study confirms that attractive individuals are commonly perceived as more trustworthy compared to their less attractive counterparts. This finding aligns with the concept of “pretty privilege,” which suggests that physical attractiveness can confer social benefits.
- Social Influence: Attractive individuals often wield greater social influence, with their opinions and actions carrying more weight in interpersonal interactions. This phenomenon extends to professional settings, where attractive individuals may be viewed as more competent and reliable.
- Implicit Bias: The research highlights the presence of implicit bias in the perception of trustworthiness based on physical appearance. Participants in the study consistently rated attractive individuals as more trustworthy, indicating the pervasive nature of “pretty privilege” in shaping societal attitudes.
- Impact on Opportunities: The perceived trustworthiness of attractive individuals can have tangible consequences, influencing opportunities in various domains such as employment, education, and relationships. This bias may inadvertently disadvantage individuals who do not conform to conventional standards of beauty.
Implications and Reflections: The findings of this research prompt reflection on the role of physical appearance in shaping interpersonal dynamics and societal perceptions. While “pretty privilege” may confer certain advantages to attractive individuals, it also underscores the prevalence of implicit biases in decision-making processes. Recognizing and addressing these biases is crucial for fostering fairness and equity in diverse contexts.
Moreover, the study underscores the importance of promoting inclusivity and valuing individuals based on their character, skills, and contributions rather than superficial attributes. By challenging stereotypes and embracing diversity, society can strive towards a more equitable and inclusive environment where all individuals are afforded equal opportunities and recognition.
In conclusion, the research on “pretty privilege” sheds light on the complex interplay between physical attractiveness and perceived trustworthiness. By illuminating the pervasive nature of this phenomenon, the study invites critical reflection on societal norms and biases. Moving forward, efforts to mitigate the impact of “pretty privilege” and promote fairness and inclusivity are essential for fostering a more equitable society.
Editor's Pick
Deciphering the Somalian Struggle: Exploring the Roots of Procrastination and Underachievement

In the global landscape of achievement and progress, Somalia often finds itself lagging behind. While many Somalis born in developed countries excel in various fields, a significant portion remains on the sidelines, seemingly unable to break through societal barriers. This phenomenon prompts a deeper exploration into the underlying factors contributing to this disparity, with procrastination emerging as a pivotal aspect.
Procrastination, a universal challenge, manifests uniquely within the Somali community, fueled by a complex interplay of cultural expectations, psychological barriers, and historical contexts. At its core, the fear of failure looms large, ingrained deeply within the fabric of Somali society. The pressure to meet familial expectations and uphold honor often paralyzes individuals, leading to a reluctance to take action.
Moreover, perfectionism exacerbates this dilemma, with Somalis striving for flawlessness in an imperfect world. The relentless pursuit of perfection creates an overwhelming fear of making mistakes, thereby perpetuating procrastination cycles. The repercussions are evident across various domains, including education, employment, and even sports.
Take, for instance, the absence of Somali representation in global sports, such as football. While numerous African players dominate top leagues worldwide, Somalis remain conspicuously absent. This absence is not due to a lack of talent or passion but rather reflects the broader procrastination tendencies ingrained within the community.

Cultural norms and societal expectations further compound this issue, creating a barrier for aspiring Somali athletes. The emphasis on academic pursuits over sports, coupled with the fear of deviating from traditional paths, stifles potential talent and perpetuates the cycle of underachievement.
However, the solution lies not only in recognizing these challenges but also in fostering a supportive environment conducive to growth and progress. By dismantling the stigma surrounding failure and embracing imperfection, Somalis can liberate themselves from the shackles of procrastination.
Implementing practical strategies, such as goal setting, time management techniques, and self-compassion, can empower individuals to overcome procrastination and unlock their full potential. Embracing a growth mindset, rooted in the belief in one’s ability to learn and improve, is pivotal in this journey towards self-actualization.
In conclusion, the Somalian struggle is multifaceted, with procrastination emerging as a significant barrier to success and fulfillment. By delving into the psychological intricacies of procrastination and its impact on the Somali community, we can pave the way for meaningful change. It’s time to decode the complexities of procrastination and chart a course towards a brighter, more empowered future for all Somalis.
Study
Over 80% of the EU’s farming subsidies support emissions-intensive animal products – new study
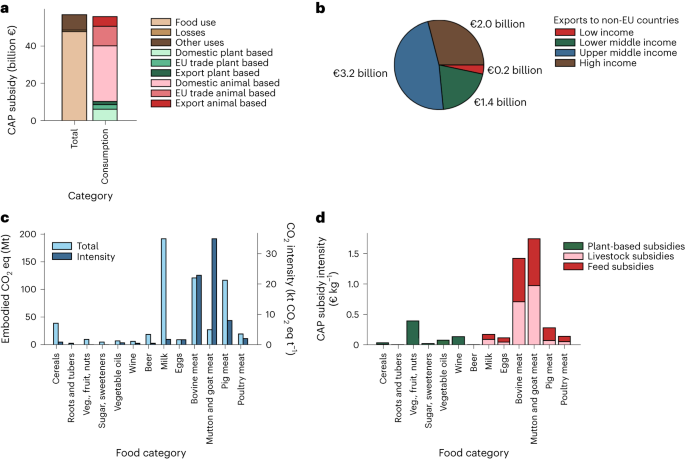
A groundbreaking study published in Nature Food reveals a concerning reality: more than 80% of the European Union‘s farming subsidies prioritize emissions-intensive animal products over sustainable plant alternatives. These findings shed light on the significant role of the EU‘s common agricultural policy (CAP) in shaping farming practices and its impact on the environment.
The CAP, which constitutes the largest single expenditure of the EU, has long been criticized for its disproportionate support of big landowners, minimal environmental provisions, and susceptibility to corruption. While efforts to introduce environmental reforms face resistance from lobby groups and farmers, the urgency of such changes is underscored by the study’s findings.
Alarmingly, the research indicates that the majority of the €57 billion annual CAP budget is channeled towards animal-based products, including beef, pork, chicken, dairy, and eggs. This staggering allocation perpetuates an uneven playing field where animal products are artificially cheaper than plant-based alternatives, distorting consumer choices and exacerbating environmental degradation.
The consequences of this subsidy structure extend beyond the EU, influencing production and consumption patterns globally. Subsidized exports to non-EU countries, totaling 12% of the CAP budget, further perpetuate unsustainable farming practices and hinder efforts to promote healthy and sustainable diets worldwide.
In the face of mounting pressure from climate-driven extreme weather events and rising production costs, the need for green reforms within the CAP is more pressing than ever. Failure to enact significant changes risks exacerbating environmental damage and undermining the long-term viability of the agricultural sector.
As advocates for a more sustainable and resilient food system, we call for urgent reforms to redirect farming subsidies towards environmentally-friendly practices and plant-based alternatives. The recent dilution of green EU policies represents a concerning regression, highlighting the imperative for bold and decisive action to safeguard our planet’s future.
-

 WARYATV Analysis4 weeks ago
WARYATV Analysis4 weeks agoHow Trump’s Broader Appeal Secured a Second Presidential Term
-

 Middle East3 weeks ago
Middle East3 weeks agoU.S. Expresses Deep Concern Over Escalating Nuclear Tensions with Iran
-

 Top stories2 weeks ago
Top stories2 weeks agoLe Pen eyes opportunity as French government teeters on collapse
-

 Middle East2 weeks ago
Middle East2 weeks agoAssad regime ends; Dictator’s plane disappears from radar after leaving Damascus
-

 Editor's Pick1 week ago
Editor's Pick1 week agoEUCAP Somalia workshop paves the way for women’s leadership in fisheries
-

 Somaliland6 days ago
Somaliland6 days agoUS Congress to Submit Motion to Recognize Somaliland’s Independence
-

 Russia-Ukraine War11 hours ago
Russia-Ukraine War11 hours agoEurope’s Leadership Test in Supporting Ukraine Against Russian Aggression
-

 Study9 months ago
Study9 months agoOver 80% of the EU’s farming subsidies support emissions-intensive animal products – new study































